Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is a method that assigns prices to products or services primarily based on the resources consumed by using exceptional activities. Unlike traditional costing methods, ABC offers an extra accurate cost illustration by way of focusing on specific procedures worried in production. It identifies various activities within a business enterprise and assigns expenses to products primarily based on real consumption.
ABC is divided into 4 types: transaction-based ABC, which allocates charges based totally at the variety of transactions or pastime frequency; period-based ABC, which considers the time taken to finish each hobby; output-based ABC, which specializes in the number of devices produced; and hybrid ABC, which combines elements from different types to match unique organizational desires.
Activity-Based Costing has numerous merits. It gives correct value facts for higher decision-making and helps in enhancing performance by means of figuring out and doing away with non-fee-introduced sports. ABC also gives better price manipulation through giving a clearer view of wherein cash is spent and assists in knowledge product profitability. The system for calculating prices in ABC is: Cost in step with Activity = Total Cost of Activity / Total Cost Driver Units.
This permits groups to decide costs for specific activities accurately. Examples of ABC software consist of manufacturing, in which prices are calculated for each production step, healthcare, in which expenses are assigned to clinical tactics, and retail, wherein charges are decided for diverse customer support sports.
While ABC has great benefits, which includes correct cost allocation, higher aid management, and better choice-making, it also has a few drawbacks. Implementing ABC is time-eating and expensive, requiring normal updates and massive resources. Moreover, there is complexity in assigning indirect expenses, which might also add to the venture. Despite these cons, ABC stays a valuable device for agencies looking to refine their costing methods and obtain greater precise value management.
What Is Activity Based Costing(ABC)?
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is a costing method that allocates costs to products and services based on the activities involved in their production. It specializes in identifying and evaluating all of the sports an organization undertakes and the sources consumed. Costs are then allocated to products or services based totally on their actual usage, supplying a more correct and particular value evaluation.
ABC is especially useful for businesses with complex production processes or high overhead costs. It gives companies better insight into which activities contribute the most to their expenses, allowing them to make more informed decisions regarding pricing, efficiency, and cost control.
How Does Uk’s Cima Define ABC?
The Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA) in the UK defines Activity-Based Costing (ABC) as a costing method that identifies activities in an organization and assigns costs to products or services according to actual consumption of resources. This method offers a greater correct photo of product and provider prices, allowing better strategic decision-making.
What Were The Reasons For Developing ABC?
The number one motive for developing ABC was to address the shortcomings of conventional costing strategies that regularly did not capture the true cost of manufacturing, in particular in complicated manufacturing environments. Activity-Based Costing (ABC) was developed in the late 1980s by Robert Kaplan and Robin Cooper at Harvard Business School.
Traditional strategies commonly allotted charges based on an unmarried fee driving force, together with direct hard work or machine hours, which brought about inaccuracies. ABC was invented to offer a more correct and fair allocation of oblique expenses with the aid of considering multiple cost drivers and sports.
What Are The Different Types Of Activity-Based Costing(ABC)?
The 4 types of activity-based costing activities are:
- Transaction-Based ABC: Assigns costs based on the number of transactions or the frequency of activities performed. Suitable for environments where costs are driven by the volume of transactions rather than their complexity.
- Duration-Based ABC: Allocates costs based on the time required to complete each activity. Effective when the time spent on activities significantly impacts costs, such as in services or custom manufacturing processes.
- Output-Based ABC: Relates costs to the number of units produced. This method is useful in industries where output volume is a key cost driver, such as manufacturing and assembly lines.
- Hybrid ABC: Combines elements of transaction-based, duration-based, and output-based approaches. This is versatile and well-suited for complex environments, where no single costing method is sufficient.
What Types Of Businesses Benefit Most From ABC?
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) benefits businesses with many processes and high indirect costs. Manufacturing agencies use ABC to locate the true cost of making each product. Service groups additionally find it helpful, as it facilitates them to recognise which activities value the most. Complex industries like healthcare and logistics use ABC to manipulate prices higher.
Companies that need accurate pricing for their products or services, especially those with high overhead costs or multiple product lines, benefit the most from ABC. Businesses looking to improve profitability and make data-driven decisions use ABC to control expenses better.
What Are The Stages Of Activity-Based Costing?
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) involves 5 stages:
- Identify activities: Determine all the activities within the organization, such as manufacturing, packaging, or distribution.
- Assign costs to activities: Allocate costs to each identified activity.
- Identify cost drivers: Determine the factors that influence costs, such as labor hours or units produced.
- Calculate the cost per driver unit: Use the formula to compute the cost of each activity per unit.
- Assign costs to products or services: Allocate these calculated costs to products or services based on their usage of the activities.
Each stage is critical to ensuring accurate costing. ABC helps companies understand which activities are the most costly and manage resources more effectively. Capitalizethings.com offers ABC solutions to corporations. For help with ABC, attain out via mail or call us at +13238569123.
What Are The 5 Steps To Implement ABC?
Implementing Activity-Based Costing (ABC) involves the following five steps:
- Identify activities: Recognize all activities that consume resources, such as manufacturing or customer support.
- Assign costs to activities: Allocate costs based on the resources consumed by each activity.
- Determine cost drivers: Identify the factors affecting the cost of activities, like labor hours or machine usage.
- Calculate the cost per driver unit: Use the formula to calculate the cost of each activity based on its driver units.
- Assign costs to products or services: Allocate costs to products or services based on their use of each activity.
These steps help organizations manage resources more efficiently and make smarter decisions about pricing and cost control.
What Is The First Step In Applying Activity-Based Costing?
The first step in applying Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is to identify the activities that consume resources. Activities are the exceptional responsibilities needed to make a product or offer a carrier. For instance, in a manufacturing facility, sports can be assembling, packaging, or exceptional checking. Knowing those sports is critical due to the fact each one has extraordinary expenses. This step is to set know-how wherein the cash is going. Once the activities are diagnosed, the following steps involve assigning costs and finding cost drivers.
When To Use ABC Costing?
ABC costing is beneficial when a business has complex processes and needs precise cost data. It is first-rate used while traditional costing methods do not deliver a real photograph of fees. Companies with many services or products, high overhead fees, or many departments use ABC to locate authentic fees. ABC is likewise beneficial when charges want to be managed intently. It helps in decision-making about pricing, price-reducing, or improving performance. Service groups use ABC to recognize charges better for services provided.
In 1988, Kaplan and Cooper developed ABC to provide better insights into overhead costs. The Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA) continues to recommend it as a method to understand resource consumption. A research paper from “Harvard Business Review” (Kaplan & Anderson, 2007) further demonstrated how ABC improves decision-making, particularly in complex manufacturing environments.
By implementing ABC, businesses have reported cost savings of up to 30% in industries like automotive and electronics. Forbes Insights (2019) also indicated that 80% of companies using ABC saw an increase in profitability within the first two years.
What Is The Formula For Activity Based Costing?
The formula for Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is designed to calculate the cost per activity by dividing the total cost of an activity by the total number of cost driver units. The formula looks like this:
Cost per Activity = Total Cost of Activity / Total Cost Driver Units
This formula helps businesses determine the precise cost of each activity involved in producing a product or providing a service. By knowing the costs tied to individual activities, businesses can improve their pricing strategies and cost management.
How Do You Calculate Activity-Based Costing?
To calculate Activity-Based Costing (ABC), follow these 5 steps:
- Allocate these costs to the products or services based on their usage of each activity.
- Identify the activities that consume resources.
- Assign costs to each activity based on the resources used.
- Determine the cost drivers that influence these activities, such as labor hours, machine usage, or materials.
- Calculate the cost per driver unit by dividing the total cost of the activity by the total number of cost driver units. Use the formula: Cost per Activity = Total Cost of Activity / Total Cost Driver Units.
This calculation gives businesses a clear understanding of the real costs involved in production, enabling more informed pricing and profitability analysis.
What Is The Example Of Activity-Based Costing?
An example of Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is a manufacturing company. The company identifies activities such as cutting, assembly, and packaging. The employer identifies exclusive activities like cutting, assembling, and packaging. It assigns expenses to those activities based totally on how a good deal sources they use.
For instance, if the packaging process costs $1,000 and involves 200 hours of labor, the cost per hour is $5. If a product takes 10 hours to package, the packaging cost for that product is $50. This helps the company understand the true cost of each product, allowing for more accurate pricing and cost control.
What Is An Example Of Activity Based Costing In The Service Industry?
In the service industry, an example of Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is a bank The financial institution identifies activities like account setup, mortgage processing, and customer service. Each hobby uses assets like team of workers time and generation. The bank assigns costs to every hobby based on its use.
For example, if loan processing costs $2,000 and takes 100 hours, the cost per hour is $20. If a loan takes 5 hours to process, the cost is $100. This helps the bank understand which services are costlier and where to improve efficiency or adjust pricing.
What Are The Pros And Cons Of Activity Based Costing?
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) has several pros and cons:
Pros:
- Provides accurate cost data by assigning costs based on actual resource consumption.
- Helps identify cost-saving opportunities by revealing which activities consume the most resources.
- Improves decision-making in pricing, product mix, and profitability analysis.
- Assists in better cost control for companies with complex production processes.
Cons:
- Fixed costs may be treated as variable costs, which can lead to incorrect conclusions in some cases.
- Time-consuming and expensive to implement due to the need for detailed data collection and analysis.
- Requires constant updates to ensure accuracy, as processes and costs change over time.
- Can be difficult to implement in businesses where cost tracing is complex or data is not readily available.
What Is Time Driven Activity Based Costing?
Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing (TDABC) is a streamlined approach to ABC that focuses on time as the main cost driver. It measures how long activities take and assigns costs based on the time consumed for each activity.
Unlike traditional ABC, TDABC simplifies the costing process by using basic data such as time estimates and cost rates, making it easier to update and manage. TDABC is beneficial for companies looking to reduce the complexity of traditional ABC and improve their cost calculations with less administrative work.
Capitalizethings.com offers TDABC services for businesses looking to simplify their costing process. Reach out through mail or name +13238569123 to study extra.
How Does ABC Improve Cost Accuracy?
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) improves cost accuracy by assigning costs based on actual usage rather than general averages. It specializes in activities and their actual costs, not just an easy common. This way, it gives a true price of each product or service. Companies can see which sports are steeply-priced and reduce them. This improves choice-making and efficiency.
Traditional costing techniques often disguise the genuine charges, however ABC makes them clean. For example, an organization can see if one product takes more assets than any other and adjust its fee or manufacturing.
According to Kaplan & Cooper’s 1988 study, Activity-Based Costing (ABC) revolutionized the way companies think about cost allocation. Their research showed that companies using ABC often see improvements in profit margins due to better cost visibility. A more recent analysis by CIMA (2020) suggests that businesses implementing ABC experience a 20-30% improvement in cost control and profitability over a 5-year period.
Also, companies transitioning from traditional costing to Time-Driven ABC have reported increased efficiency and better cost management. A case study from Harvard Business Review (2021) noted that a mid-size manufacturing firm using TDABC reduced their cost tracking time by 50% and improved decision-making speed.
What Are The Challenges Of Using ABC?
The challenges of Activity-Based Costing (ABC) include the time-consuming nature of its setup because it requires detailed data collection on activities. First, it can be time-consuming to install because it needs certain statistics on activities. Second, tracing charges to every pastime is hard, specifically in massive companies with many strategies.
Third, a few fees which are constant can be wrongly handled as variables that lead to errors. Transitioning to computerized ABC accounting also can be difficult and high priced. It desires software programs and body of workers training. Despite these challenges, ABC can offer higher value statistics for selection-making.
In a study by Kaplan & Anderson (2023), it was noted that companies implementing automated ABC systems saw improved financial management, but nearly 70% struggled with the cost and complexity of setup. This highlights that while ABC is beneficial, the initial investment in terms of software and expertise needs careful consideration.
Which Sectors Show The Highest Prevalence Of ABC?
ABC is most commonly used in sectors where costs are complex, such as manufacturing. The production sector indicates an excessive occurrence of ABC because it facilitates in assigning fees appropriately. The carrier region, specially healthcare and banking, additionally uses ABC extensively to manipulate fees and apprehend carrier pricing higher.
Other sectors like telecommunications, logistics, and authorities use ABC to control spending and enhance efficiency. Regions like North America, Europe, and elements of Asia show better use of ABC due to their complex industries and consciousness on fee control.
Why Do Service Companies Use ABC?
Service companies use Activity-Based Costing (ABC) to determine the true cost of services, which are often difficult to measure due to reliance on labor and time. Unlike products, services are frequently hard to value because they rely on hard work and time. ABC helps carrier agencies find which activities value greater. For instance, a financial institution can see if customer service takes an excessive amount of time and resources.
ABC allows in setting fair fees and handling expenses. It also helps in making higher choices approximately which offerings to provide or enhance. Capitalizethings.Com helps provider businesses use ABC to manipulate expenses. Reach out via mail or call us at +13238569123 for more info.
ABC not only aids in cost reduction but also in pricing strategies, ensuring that companies can align costs with customer expectations. According to a report by CIMA (2022), companies in the service sector saw a 15% improvement in profitability after adopting ABC.
What Is Activity Based Costing In Management Accounting?
In management accounting, Activity-Based Costing (ABC) enables managers to make better decisions by providing more accurate cost information. ABC breaks down costs with the aid of every activity, not simply with the aid of departments. This offers a clearer photograph of where money is going.
It suggests which services or products are profitable and which of them aren’t. This facilitates managers in budgeting, pricing, and price control. It is different from traditional methods that hide the real fees. For organizations wanting to apply ABC in management accounting, Capitalizethings.com gives professional steerage and services.
What Are The Limitations Of Activity Based Costing?
The limitations of ABC include the misclassification of fixed costs as variable, leading to errors in cost management. First, it so often treats fixed fees as variable costs, that could cause errors in decision-making. Second, tracing costs to unique activities can be hard, especially in large groups. This can cause inaccuracies. Third, transitioning to automatic ABC accounting is hard. It wants software programs, education, and investment, which is luxurious for some companies. Despite those barriers, ABC facilitates groups to apprehend fees better.
What Are The Alternatives To Activity-Based Costing (ABC)?
There are numerous alternatives to Activity-Based Costing (ABC) like traditional costing, job order costing, process costing, standard costing. Traditional Costing assigns charges based on direct expenses like hard work and materials. It is easy however now not always correct. Another choice is Job Order Costing, which tracks charges through particular jobs or batches, useful for customized manufacturing.
Process Costing is some other alternative, nice for groups with non-stop manufacturing methods. Standard Costing uses widespread prices as opposed to real charges and is ideal for cost management. Each alternative has its blessings and downsides, and the choice depends on the enterprise’s needs.
A 2021 study by the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants revealed that businesses shifting from ABC to Standard Costing saw a 20% reduction in operational complexity, although cost accuracy was compromised.
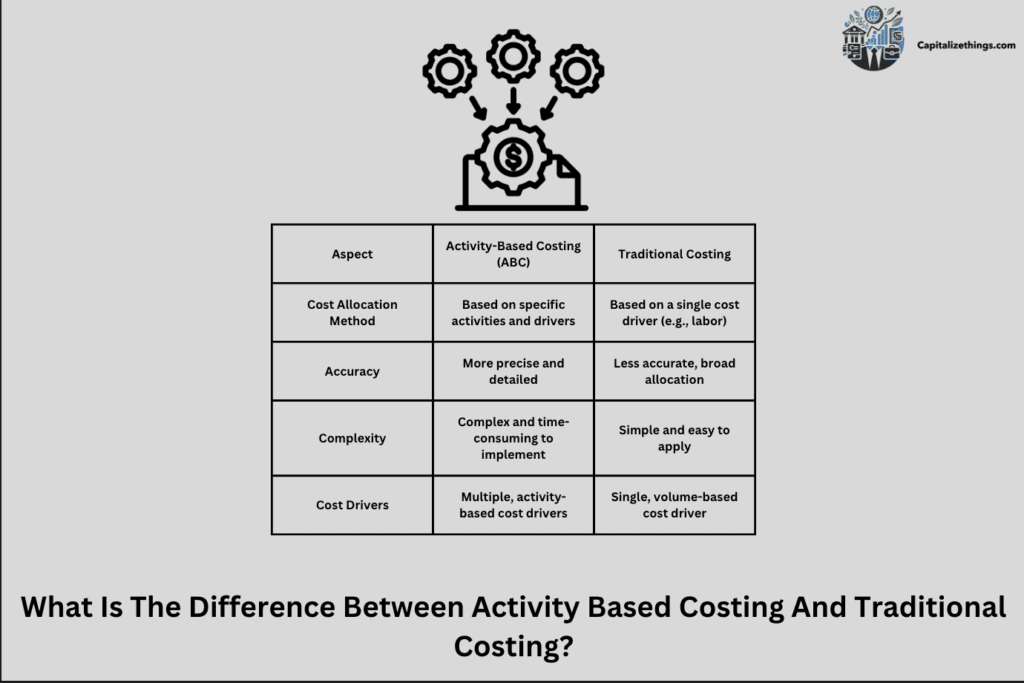
What Is The Difference Between Activity Based Costing And Traditional Costing?
The primary distinction between Activity-Based Costing (ABC) and Traditional Costing lies in how costs are allocated.. ABC assigns charges based totally on sports and their real use of resources, imparting accurate cost records. Traditional Costing assigns charges based on an easy price, like direct labor hours or machine hours. This can hide genuine prices and lead to bad decisions.
ABC is higher for agencies with complex procedures, whilst Traditional Costing is easier and inexpensive. Each method has its uses, and the selection depends on the business enterprise’s desires.
How Common Is The Use Of Activity-Based Costing (ABC)?
The use of Activity-Based Costing (ABC) varies throughout regions. It is usual in North America and Europe, wherein businesses cognizance of cost manipulation and performance. These regions have industries like production, healthcare, and finance, which gain most from ABC.
In other continents, like Asia, using ABC is developing but continues to be much less common. Over time, more companies are adopting ABC as they look for better cost management methods. Capitalizethings.com offers services to help agencies enforce ABC correctly. Contact us through mail or call +13238569123 for extra facts on a way to get started.
How Has The Adoption Of ABC Changed Over Time?
The adoption of Activity-Based Costing (ABC) started in the late 1980s, driven by the need for better costing methods than traditional approaches. Over the years, greater corporations have followed ABC as they search for accurate ways to manipulate prices and enhance efficiency.
Technological improvements have made ABC easier to apply with automatic systems. However, the adoption rate nonetheless varies by way of place and industry. In North America and Europe, its use is more substantial. In other parts of the world, the growth is slower but steady.
What Is The Role Of Lean Accounting As An Abc Alternative?
The role of lean Accounting as an ABC alternative is a cost management method focused on reducing waste and simplifying processes. It aligns with lean production by imparting easy monetary reports. This technique offers higher choice-making aid by using those that specialize in fee-introduced sports. Unlike Activity-Based Costing (ABC), Lean Accounting reduces overhead prices with the aid of putting off wasteful practices.
It helps agencies understand their prices, including direct expenses and overhead charges, without complicated calculations. It additionally considers the Theory of Constraints (TOC), which specializes in bottlenecks that slow manufacturing.
This method is higher for corporations aiming for continuous improvement. Lean Accounting helps companies recognize purchaser cost and economic value brought. It aligns with Peter F. Drucker’s thoughts in “Management Challenges.” Lean Accounting is less difficult and specializes in value performance as opposed to specified cost allocation.
What Is An Activity-Based Cost Accounting System?
An Activity-Based Cost Accounting System assigns costs to products and services based on the activities involved in production. It isn’t like traditional value management systems, which regularly allocate charges primarily based on one motive force. This method looks at resource intake, such as indirect prices (overhead) and direct fees. It tracks costs for every interest in the manner.
The Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA) defines it as a machine that makes use of value drivers to assign overhead prices. It enables corporations to recognize where money is spent.
This device makes use of information series to determine the authentic price of production. Robin Cooper and Robert S. Kaplan advanced it to provide greater correct prices. It gives accountants higher data to manipulate prices.
What Are The Benefits Of Using An Activity-Based Cost Accounting System?
An Activity-Based Cost Accounting System helps companies see their true costs, including fixed and variable costs. It suggests how much each hobby expenses, inclusive of fixed and variable fees. This helps organizations control overhead prices and improve profits. It gives better insights than traditional systems. It suggests where cash is wasted. This gadget helps inside the manufacturing zone and provider industries. It aligns with Kaplan’s balanced scorecard, which makes a speciality of common performance. It helps strategic selections by presenting more accurate fee facts.
Companies also can see the monetary cost added by means of every interest. It helps corporations make smart changes to lessen costs. With better fee allocation, corporations can pay attention to what adds the maximum value. The device is distinctive however in cost management.
What Are The Key Components Of An Activity-Based Cost Accounting System?
The key components of an Activity-Based Cost Accounting System include activities, cost drivers, overhead costs, and data collection. These components include activities, fee drivers, overhead expenses, and value allocation.
Activities are the steps needed to make a service or products. Cost drivers are factors that purpose costs, like machine hours or hard work. Overhead costs are indirect prices, like utilities. The gadget additionally includes direct costs, like substances. Data series is any other key component.
It includes accumulating facts to assign fees correctly. This device also makes use of management reports to reveal price details. The Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA) makes use of these additives to outline the device. Accountants use these additives to improve fee management. Firms can see which sports use the maximum assets and modify their procedures.
What Is The Difference Between Activity Based Costing And Value Stream Mapping?
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) and Value Stream Mapping are both geared toward understanding costs and processes, but they focus on different aspects. ABC makes a speciality of cost allocation based totally on activities and price drivers. It seems at each direct and oblique charge. Value Stream Mapping focuses on waft in this manner. It identifies waste and regions for improvement. It aligns with lean manufacturing concepts, like lowering waste. Value Stream Mapping is more visual. It indicates how services and products pass through a process.
ABC is more special in cost analysis, searching at overhead charges and direct prices. Value Stream Mapping enables in understanding normal performance. Peter F. Drucker’s management ideas guide both methods for higher procedure control. ABC looks at charges, even as Value Stream Mapping looks at method drift and efficiency.
What Is The Difference Between Activity Based Costing And Value Stream Costing?
The difference between both Activity-Based Costing (ABC) and Value Stream Costing help companies understand costs, but they work differently. ABC assigns expenses primarily based on sports and makes use of cost drivers. It consists of direct prices and indirect prices (overhead). Value Stream Costing makes a speciality of the value of whole processes or cost streams. It aligns with lean manufacturing and gets rid of waste. ABC looks at information for each activity, whilst Value Stream Costing looks at the general fee of the method.
The Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA) indicates ABC for specific price management. Value Stream Costing is easier and higher for companies focusing on lean methods. It appears at fixed charges and variable fees in a broader view. Both methods assist companies understand charges higher.
What Costs Are Not Assigned To Products In Activity-Based Costing?
In Activity-Based Costing (ABC), some costs are not assigned to products like General administrative expenses and indirect costs such as office supplies or utilities may not be allocated to products, as they are not directly related to production. These fees do no longer at once relate to manufacturing. Indirect charges, along with utilities and office components, also not be assigned. Fixed expenses that do not alternate with production volume stay unassigned. ABC makes a speciality of direct costs, like materials and exertions, and pastime-based total costs.
It makes use of cost drivers to allocate charges more as it should be. It does not assign prices unrelated to the sports that create prices. This approach helps companies apprehend which charges are associated with specific services and products. Robin Cooper and Robert S. Kaplan developed ABC to improve cost control by using that specialization in applicable charges.
How Can Activity Based Costing Be Used In Service Companies?
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is useful in service industries like finance and healthcare because it assigns costs based on activities involved in delivering services. It helps in knowing the costs of different offerings. ABC assigns expenses based totally on sports, like customer service or transaction processing. It considers both direct and oblique costs, like labor and utilities. Service companies use price drivers to allocate expenses more as they should be. This enables them to apprehend customer costs and improve pricing. ABC affords better price data than conventional structures.
It facilitates in coping with overhead charges and enhancing offerings. Accountants use ABC to analyze value statistics and make higher decisions. Firms can see the monetary cost added by each carrier. ABC aligns with control accounting principles and helps in turning in cost-green services. It supports choice-making and strategy.
Conclude:
Activity-Based Costing (ABC) and its alternatives like Lean Accounting and Value Stream Costing are essential for contemporary organizations. ABC enables firms to assign prices as it should be to products and services via focusing on sports and resource intake. This method improves value management, specifically in complex environments where traditional cost systems fall quickly. It helps in identifying fee drivers and lowering overhead prices, which enhances profitability. Lean Accounting, alternatively, focuses on casting off waste and is aligned with lean production principles.
Value Stream Costing looks at the general value of procedures, imparting a broader view of performance. Each method has its strengths, and businesses ought to select primarily based on their unique desires. By information these unique methods, businesses can obtain higher economic overall performance, powerful value manipulation, and strategic choice-making. These techniques are gear for developing monetary cost and helping boom in aggressive markets.

Larry Frank is an accomplished financial analyst with over a decade of expertise in the finance sector. He holds a Master’s degree in Financial Economics from Johns Hopkins University and specializes in investment strategies, portfolio optimization, and market analytics. Renowned for his adept financial modeling and acute understanding of economic patterns, John provides invaluable insights to individual investors and corporations alike. His authoritative voice in financial publications underscores his status as a distinguished thought leader in the industry.