Financial Ignorance involves failing to build solid financial resources for yourself or your firm. Money issues are more complex than ‘not having the ability to read or write. We must note that it affects all ages and occupations.
Financial Ignorance can hurt you by affecting your financial health. Insufficient emergency funds or retirement possibilities can result from poor planning and handling of finances if you don’t comprehend commercial financial products and services. If you don’t grasp the frequently intricate financial goods and services provided to you, exorbitant interest rates, growing debt, and scams could snowball your money difficulties. Additionally, financial illiteracy could render it tougher to recover from financial problems.
An example of financial Ignorance is an individual who is not aware of financial matters like transactions, paying bills, and managing expenses.
What is financial Ignorance?
Financial ignorance is the inability to understand economic processes and make informed financial decisions. Many consumers get confused by financial services and products. Financial ignorance is crucial to address because there are numerous items and credit options that people need to understand.
What causes financial illiteracy?
The 4 main causes of financial illiteracy are:
- Race and ethnicity disparities
- Financially Illiterate Parents
- Heavy Financial Stress
These issues make it hard for individuals to grasp basic financial principles.
Why are so many people financially illiterate?
So many people are financially illiterate because a significant percentage of the population is neither taught nor wants to develop financial literacy, even though it would benefit them much. They may learn enough to be harmful, but full literacy takes time and motivation, and only some people have the time or enthusiasm to learn about finances. I thoroughly researched many life insurance policies in my 20s, surprising the agents attempted to sell me them. It saved me from expensive options. The closest I got to financial literacy was in my 50s. The topic intrigued me.
Why aren’t people interested? People avoid financial literacy because it involves complex topics like math, risk management, and economics.. To make matters worse, many people profess to be financial education experts but are selling something. Free financial issues seminars, radio and internet shows, and newspaper columns are sales pitches. Most consumers must avoid these salespeople (or criminals) to discover better financial instruction.
What are the effects of a lack of financial literacy on young adults?
Financially illiterate youth face higher risks of debt, poor financial decisions, and missed opportunities for wealth-building. These issues affect low-income and marginalized families, increasing their vulnerability to predatory lending, costly debts, and long-term financial instability. Lack of financial knowledge can also prevent wealth-building and entry to higher learning and professional development.
Financially illiterate youth are more likely to slip into poverty and debt. Bad spending and borrowing behaviours can lower credit scores, increasing financial instability. Financial literacy encourages adolescents to overcome economic hurdles and live financially secure lives, closing the opportunity gap in marginalized communities.
If you’re a young adult struggling to understand financial basics, reach out to our experts at capitalizethings.com via email before calling +1 (323)-456-9123. We offer a free 15-minute consultation to help you assess your current knowledge and start building a strong foundation in financial literacy.
What financial issues are today’s youth facing?
3 most common financial issues that are being faced by youth now a days are:
- Repaying student loans
- Learning Investment and Risk-Taking
- Avoiding Pressure to Follow a Worn Path
1. Repaying student loans
Student loans are one of the major issues many young people confront in an age when an undergraduate degree is no longer enough in many areas.
Attorney Shane Fischer of Winter Park, Florida, says many students are taking out excessive loans to pay for a higher education that will not pay for itself no matter how good a job they get after graduation due to the pressure to go to a reputable school and compete for restricted opportunities. Knowing what I know now, I would have chosen a public school over an expensive private institution.
Graduate school debt averages $37,650 per person. The average new graduate educational loan debt-to-income ratio is 63%. In the fourth quarter of 2023, there was $1.6 trillion in US student loan debt.
2. Learning Investment and Risk-Taking
The Great Recession affected many Gen Yers who couldn’t find work or watched their parents’ financial profits plummet. Rachel Cruze, a personal economics expert and daughter of Dave Ramsey, thinks the economic slump has made many young folks afraid to invest in stocks. Stock market investing requires long-term thinking. Despite challenging years, stocks have made money. Cruze says spending early and often can help young people accumulate wealth later in life.
3. Avoiding Pressure to Follow a Worn Path
Matthew B. Brock, CFP, senior partner and founder of Divergent Planning in Bethesda, Maryland, thinks cultural expectations constitute a significant obstacle. Brock claims Generation Y is advised to plan financially. An older generation whose financial standing needs to prove their method right often gives this advice.
Brock says young adults don’t want to continue keeping up with the Joneses because they lost their jobs and houses and may never leave their jobs. Gen Yers choose independence and exposure over property ownership. Brock said most young adults wait longer to marry, move to the suburbs, and have kids.
Renting allows them to quit a job, relocate to another city, save up, and take a few months off to explore or start a business. A car, house, and high salary are not usually part of the American Dream. Freedom means doing whatever makes you happy. Brock argues older generations should acknowledge that younger people may define happiness better than they do.
What are the consequences of being financially illiterate?
Financial illiteracy leads to poor savings, overspending, and unwise credit decisions, often resulting in debt. Family economic stress can cause divorce, committing suicide, assault in the home, and other crimes.
The recent economic crisis and the growing complexity of the banking system demonstrate that our youth’s financial knowledge and abilities are crucial to our nation’s future success and financial security. Like reading and writing, financial education affects students’ well-being and our communities’ economic and social fabric. This is particularly true for non-English speakers.
The financial literacy crisis in our country is growing. The results are more credit card debt, bankruptcies, and decreased savings. According to the Federal Reserve, Most bankruptcy-filing families owe more than 1.5 times their yearly income in short-term, high-interest debt. Even highly educated, high-income folks may need to learn how to budget or handle their money. Financial illiteracy affects all income levels. Young adults spend $150 billion yearly, according to 2010 estimates. Online shopping and gambling, relentless credit card advertising, and electronic phishing schemes have made our youngsters easy prey.
It is crucial to grow our pupils’ financial knowledge and skills. Students must understand earning and expenditure, saving and investing, borrowing wisely, college costs, and financial scams to make good financial decisions.
How does financial illiteracy affect people?
Financial illiteracy typically results in debt accumulation and financial insecurity. Without knowledge of financial principles, many fall into traps like high-interest loans and payday advances.
What can a lack of financial literacy cause you to lose?
Financial illiteracy can cost you your assets and lead to poor financial decisions, like mismanaging or overspending finances. People risk losing cars, homes, and other assets due to their inability to manage finances properly.
Without strong financial literacy, you may lose out on essential budgeting skills. Speak with our budgeting experts at capitalizethings.com by calling at +1 (323)-456-9123 or email us for a complimentary 15-minute consultation before you proceed.
What are the long-term societal impacts of financial illiteracy?
The 5 long-term societal impacts of financial illiteracy are:
- Poor retirement planning
- Missed savings or investments
- Lack of budgeting and impulse spending
- Slower career growth
- Financial hardship increases vulnerability.
1. Poor retirement planning
Only some realize the value of early retirement planning. Over time, this mistake has serious repercussions. Without a solid grasp of investment possibilities, the concept of compound interest, and the power of regular saves, people risk retiring broke. This leaves retirees relying on state pension or fighting to make ends meet.
2. Missed savings or investments
Financial Ignorance typically prevents investment. People who don’t know about investment funds, property, or pensions may miss out on profitable chances, limiting wealth generation and financial stability.
3. Lack of budgeting and impulse spending
Lack of financial education can lead to bad money management. Impulse buying and no budget are examples. Without knowing needs versus wants and saving, people may live pay check to pay check and be unable to save for emergencies. Save at least three months’ net income.
4. Slower career growth
Financial illiteracy can affect careers. Without negotiation skills, professional development, and an awareness of the long-term economic ramifications of employment decisions, people may miss out on pay advancement, career growth, and financial success.
5. Financial hardship increases vulnerability.
Financially illiterate people may need help with economic issues. Financial storms like recessions, job losses, and unanticipated bills can leave folks without financial knowledge unprepared. That vulnerability can cause stress, broken relationships, and a protracted recovery.
Why is lack of financial education a problem?
Lack of financial education leads to debt, overspending, and financial instability. Without literacy, individuals face difficulties managing money, which can lead to long-term financial crises.
Statistics from the Federal Reserve show that the average family filing for bankruptcy owes 1.5 times their annual income in high-interest debt (Federal Reserve, 2023). This highlights how financial illiteracy affects not only low-income families but also those who are highly educated. The average credit card debt per household reached $5,733 in 2022, adding to the overall financial strain on young adults.
A 2020 study by the National Financial Educators Council found that 62% of U.S. adults reported financial stress as a major issue in their lives, further emphasizing the importance of improving financial literacy at all levels.
Why is financial literacy a problem in America?
Financial literacy is a problem in America because many Americans lack fundamental financial information, which contributes to our money problems—high debt, low savings, and unwise investment decisions. However, we may have learned something. Many individuals have taken money management classes, but perhaps they are not enough to stick.
What to do when a family member is financially irresponsible?
When a family member is irresponsible of his/her financial duties, Parents, siblings, and relatives may want to aid each other financially, especially if it’s another monetary contribution for an adult kid. We should aid if we can. Giving is better than receiving, etc.
While it’s natural to want to help, especially in difficult times like the COVID-19 pandemic, financial aid without clear boundaries can harm both parties. According to a 2021 CreditCards.com poll, 45% of parents gave their adult children financial support, and the average amount given was $4,154. However, without agreed-upon limits, your assistance can threaten relationships and hinder financial independence.
What is the problem with financial illiteracy?
The problem with financially illiterate individuals is that such individuals more likely to accumulate unsustainable debt due to poor spending habits or lack of long term planning. This can lead to consequences like bad credit, foreclosure, and other financial struggles. Fortunately, resources for financial education, such as those from the Financial Literacy and Education Commission, are more available than ever.
What happens when you ignore Honda Financial Services?
When you ignore honda financial services they charge late fees after 10 days. However, if paid within 29 days, late payments have little impact on your credit score.
What is the statistic of people who ignore financial advice?
Around 75% of clients ignore financial advice from consultants. A study by Charles Stanley and AKG revealed that 75% of residents have not obtained financial guidance in the last five years, while inflation shifting the playing field, leaving one in ten regretting it. The study report ‘Future of Advising – State of Flux’ examines the US advising market from both consumer and adviser perspectives and examines its prospects and challenges. Of the 2000 consumers surveyed, 55% had never seen a financial adviser, and 20% had seen one but not spoken with one in the past five years.
We’ve gone from ultra-low interest rates caused by central bank monetary policy during the 2008-9 Global Financial Crisis to prolonged high inflation, raising interest rates in most industrialized economies. High inflation has caused market volatility and higher energy and mortgage prices.
In this challenging environment, over 10% of respondents would have preferred not to seek financial assistance on a critical economic decision like retirement planning. They regretted that they had misjudged inflation (31%) and that they did not have sufficient funds saved to retire comfortably (35%).
Other causes included losing money (27%), buying the wrong product (25%), or not buying the right product (21%) due to needing more professional guidance. This group of investors would have sought advice on financial planning (31%), investing and savings (35%), and pensions (32%), according to the data.
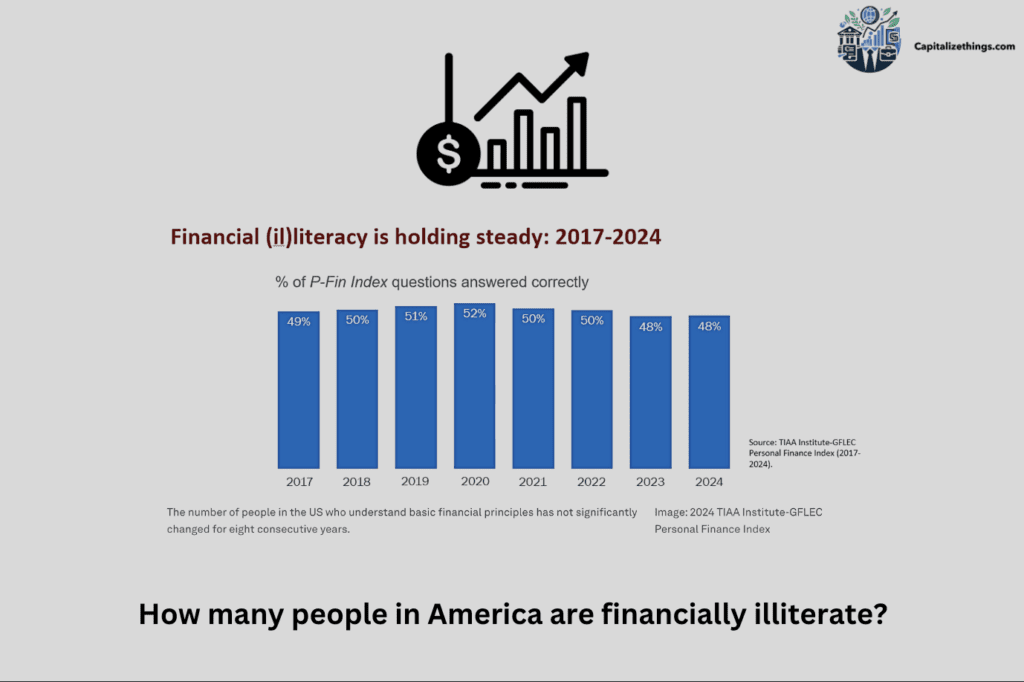
How many people in America are financially illiterate?
In America 43% people are financially illiterate. Only 57% of US adults are financially literate. Washington, Alaska, DC, and South Dakota have the lowest financial literacy rates, while Missouri, Utah, and Virginia have the highest. Roth IRAs, money-market funds, and savings accounts with high yields are new to 40% of Americans, yet over 70% of 401(k) users don’t use them.
According to FINRA Foundation data, financial literacy among US adults is declining. In 2009, almost half of adults understood financial dangers; by 2021, only 42.1% did. The chart below shows the rate of illiteracy from year 2017 to 2024.
How much does a lack of financial knowledge cost Americans?
According to 2021 and 2022 surveys, Americans lost an average of $1,819 due to financial ignorance. This is up from $1,389 in 2021, highlighting the rising costs of financial illiteracy. The US needs more financial education due to debt from credit cards (over $1 trillion), emergency savings deficits, and retirement savings shortages.
This survey could overestimate losses since people with low financial literacy may need to realize how much it costs. Lack of financial awareness can result in exorbitant interest rates, bank overdraft fees, theft of identification, and vehicle impoundment, which may not be estimated.
Financial literacy gaps could cost Americans thousands in missed opportunities and poor decisions. Let our professionals guide you—reach out or call +1 (323)-456-9123 before using the number to claim your free 15-minute consultation from our team at capitalizethings.com.
How much of America is struggling financially?
Over 25% of US individuals struggle financially. In December 2023, 72% of Americans reported being okay or comfortable, according to Federal Reserve data.
Why are young adults struggling financially?
Young adults often struggle because they lack financial education at home. When I talk to young people, they often think that certain services are free for the elderly (65 and older) and fail to comprehend why they must pay. I instruct them to share their knowledge.
What percentage of the world is financially illiterate?
33% of adults worldwide are financially illiterate, which is roughly 3.5 billion people in emerging economies.
Financial illiteracy does clear harm. Lifelong financial hardship, living paycheck to paycheck, is the most prevalent scenario, but it may worsen. Getting laid off or experiencing a medical emergency can result in debt without rainy-day money. Many in such positions fall into true poverty, which contributes to social and generational disadvantage, marginalization, and social immobility. Thus, the next generation is often deprived of excellent schooling and financial literacy, creating a vicious cycle.
The effects affect more than just the individual and their family. Financial illiteracy, especially in this widespread society, cripples democracy and ensures that real prosperity and economic growth can never come.
What is the financial illiteracy rate in India?
Financial literacy is 20.8% moderate and 42.8% elementary in India. A third of people are financially ignorant, and 4.2% have high financial literacy. Financial education requires a major revamp. Finance literacy requires a holistic approach from stakeholders. The government, Reserve Bank of India, SEBI, Insurance Regulatory and Research Authority, and industry entities run financial literacy programs. Target product categories and spread information. Daily public events improve financial awareness nationwide. However, financial literacy projects take a lot of work to measure.
A poll found 57% of Americans financially illiterate. An equity cult exists in that country. Reconsider financial literacy if its current form is staying the same.
Financial literacy is daily. You need information and risk tolerance to make financial decisions. Most importantly, choose wisely. Current programming targets English-speaking, affluent, urban audiences. Every financial literacy bundle has a regional translation. Dash and Ranjan’s research shows that non-metro and other centres would take time to catch up. The government must consider an integrated financial literacy strategy. The central government in New Delhi is responsible. Financial literacy must be preserved from fragmentation.
You can handle your money using insurance, a bank account, and stockbroking. The integrated strategy should prioritize financial literacy and associated outcomes over industry and goods. A standing committee of experts reporting to the finance minister can create comprehensive guidelines. Mutual funds and insurers can be incentivized to develop a financial literacy content strategy. The fragmented approach creates online and social media fraud. While some assist you in progress, outcome-based information is rare.
Is financial literacy a problem in India?
The NCFE found that only 27% of Indian individuals are financially literate, indicating a significant financial literacy crisis.
What is financial exclusion in India?
People and groups who lack access to financial services are financially excluded. Examples include savings accounts, financing, cashless transactions, credits, and other banking services. People are excluded from formal banking due to their socioeconomic condition and inability to meet requirements. This is a significant issue since complete communities cannot engage in the financial industry issue. Financial exclusion prohibits these populations from expanding a business, paying for college, or taking other steps to improve their quality of life.
Research by Dr. Raghuram Rajan (former RBI Governor) and the Committee on Financial Sector Reforms (2009) identified that informal moneylenders still serve about 40% of India’s population, highlighting the depth of financial exclusion.
How do you mentally deal with financial stress?
The key strategies to manage financial stress are to maintain social connections, stay physically active, and seek professional help when needed. If you have extra time without work, exercise can boost your mood. Are you getting into debt? Get help prioritizing. People with anxiety may avoid socializing. Some people need more confidence driving or traveling. If this happens, experiencing these events usually helps.
Alcohol can cause problems for money-conscious folks. You may drink more to cope with your feelings or kill time. However, drinking will not solve your difficulties and may increase your stress. Wake Up at your usual time and follow your regimen. If you lose your pattern, you may stop cooking, skip breakfast since you’re still in bed, or consume snacks instead of meals.
According to the American Psychological Association’s 2023 Stress in America survey:
- 72% of adults report feeling stressed about money
- Financial stress leads to:
- Sleep problems (55%)
- Relationship conflicts (41%)
- Depression symptoms (38%)
Research by Dr. Sarah Newcomb, behavioral economist at Morningstar (2022), shows that developing financial coping strategies can reduce stress levels by up to 40%.
How to be happy when you are financially stressed?
The primary way to maintain happiness during financial stress is to open up and communicate about your financial challenges with trusted people. You may feel unpleasant about sharing your income or expenses, ashamed about financial mistakes, or humiliated about not supporting your family. But avoiding problems will increase your financial stress. Many individuals struggle without fault in the current economy; others will likely understand your issues.
Talking to a trusted friend or family member about money can assist you relax and gain perspective. Keeping money issues to yourself makes them feel insurmountable. Talking to somebody you trust can make your concerns appear less scary. Financial issues affect the whole family, so getting their help can be vital. Even if you pride yourself on independence, inform your family of your finances and how they may help you save. Study by Dr. Bradley Klontz, Financial Psychologist (2022), found that financial transparency with family members leads to better financial decisions in 73% of cases.
What is an example of financial illiteracy?
The most common example of financial illiteracy include inadequate retirement savings, overspending, and poor long-term financial planning.
According to the National Financial Educators Council (2023): Top signs of financial illiteracy are:
- No emergency fund (64% of Americans)
- Credit card dependence (55%)
- No retirement planning (40%)
- Unable to budget effectively (38%)
Research by FINRA Investor Education Foundation (2024) indicates that financial illiteracy costs the average American $1,819 annually in fees and poor financial decisions.
How much does a lack of financial knowledge cost Americans annually?
A lack of financial knowledge costs Americans an average of $1,819 annually, according to a 2022 survey by the National Financial Educators Council (NFEC)
What percentage of high school students lack basic financial literacy?
22% of high school students need more basic financial literacy.
What is the financial literacy index of Singapore?
40% of Singaporeans are knowledgeable about finances using SKBI-GFLEC Sustainable Investments Survey data. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) and Singapore Management University’s joint study (2024) shows:
- Seniors (51+): 37% literacy rate
- Young adults (25-35): 45% literacy rate
- Middle-aged (36-50): 38% literacy rate
What is meant by financial resilience?
Financial resilience is the ability to withstand and recover from financial setbacks and life circumstances that affect income and assets. Financial stressors like unemployment, disability, divorce, and illness influence individuals. Stock market downturns, Recessions, and terrorism affect society. Dr. Sharon Danes, a University of Minnesota scholar and Extension specialist, uncovered five traits that boost resilience to life’s obstacles. Its five types are focused, Positive, flexible, planned, and proactive.
Research by Dr. Sharon Danes and The University of Minnesota (2023) also shows that households with high financial resilience recover 2.5 times faster from economic shocks.
What is resilience in the financial system?
A resilient financial system can handle diverse shocks while maintaining functionality. It will boost long-term growth, helping the economy recover and eliminating shock-related economic scarring. In other words, solid foundations make shocks simpler to absorb and handle. Where to set resilience is crucial in the terrible tail of the distribution of outcomes.
The response depends on the purpose, in this case, policies for the public, and this is one of the fundamental developments of macro-prudential planning over the previous decade. It ensures banks can lend to the economy, enterprises, and households at the desired resilience level, not only averting institution failure. We have resolution tools for locations throughout the tail of the distribution above the designated point. As banks boost their liquidity and capital buffers, resilience costs money. The benefits to society and firms should offset that expense. The resilience point must match the cost-benefit case.
The post-global financial crisis years have been spent implementing resilience in financial stability, but we must always allow for and comply with innovation. First, this work aims to strengthen counter-cyclical capacity. This means that banks can lend during severe financial crises, insurers can maintain financing capacity despite a wide range of serious shocks, and financial markets can function as they adjust to shocks, such as clearing house infrastructures. Research by Dr. Mark Carney, former Governor of the Bank of England (2023), demonstrates that resilient financial systems reduce economic recovery time by 40% after major shocks.
How to fix financial illiteracy?
Financial illiteracy can be fixed if you follow below 5 steps:
- Listen to finance podcasts
- Read finance books
- Use social media
- Budget
- Consult a financial advisor
1. Listen to finance podcasts
Podcasts can provide financial news while you clean, run errands, or stroll the dog. Most podcast applications and music streaming providers offer financial expert podcasts. Learn practical money management methods, easy financial reasons, and family financial literacy. See US News and World Report’s Best Personal Finance Podcasts for ideas.
2. Read finance books
Personal finance books abound. Find the finest personal finance books for budgeting, saving, debt repayment, first-time investing, and wealth creation on Insider’s list.
3. Use social media
According to a 2023 Forbes Advisor poll, 79% of 18-41-year-olds use YouTube, Reddit, and TikTok for financial knowledge. Follow financial specialists, get access to fascinating news, and watch financial videos on your favourite social media networks. Check out a personal finance group on Facebook for community discussions and resource sharing. Follow us on Facebook and LinkedIn for financial wellness and future security topics.
4. Budget
Expert financial advice is only helpful if you know where your monthly money goes. Use a spreadsheet or online tool to budget your income and expenses. Your budget helps you understand your expenditures and pay check distribution. With this knowledge, you can identify areas that need tightening or possibilities to save more.
5. Consult a financial advisor
A financial professional can assist you learn finance. They can answer every day and long-term financial questions. You can discuss a plan to meet your financial needs and stay on track. Keep studying finance, regardless of level. Lifelong learning and financial innovation may improve your health. Every financial control step is good. Knowledge helps you make better financial decisions during your life.
Fix financial illiteracy by consulting a financial advisor at CapitalizeThings.com: Reach out to us via email at +1 (323)-456-9123 for a free 15-minute consultation with our experts before you hire. Let us guide you on understanding the basics of budgeting and investing.
Why is financial literacy so critical?
Financial literacy is critical because it helps people prevent costly mistakes, prepare for emergencies, and make informed decisions. Traditional IRA contributions can’t be withdrawn until retirement, but floating-rate loans may have to change interest rates each month.
Financial decisions that seem harmless to someone unfamiliar with these and similar financial facts may cost them money or affect their life plans. Financial knowledge helps people avoid financial blunders.
Financial literacy prepares for emergencies. Saving and emergency preparedness prepare people for uncertainty. A job loss or considerable expense can be financially devastating, but saving regularly might help. Financial literacy helps people achieve goals. Understanding how to plan their finances and save money helps people set expectations, hold themselves accountable, and achieve financial goals.
Financial awareness boosts confidence. Imagine making a life-changing financial decision with more knowledge. With financial understanding, people may make life decisions more confidently. They’ll be more likely to succeed and less upset by unexpected results.
FINRA Foundation Research (2024) quantifies the impact of financial literacy:
- Financially literate individuals save 40% more for retirement
- They pay 35% less in transaction fees and costs
- Have 32% less credit card debt
- Are 28% more likely to have emergency savings
What does Robert Kiyosaki say about financial literacy?
According to Rich Dad, Poor Dad author Robert Kiyosaki, income, expense, liability, asset, and cash flow are the six keys to financial education and literacy. Kiyosaki considers six keywords crucial, including the last “key”—a two-word combination. Check out the video below to learn about financial literacy from robert kiyosaki.
How do financial institutions affect your budget?
Financial institutions impact your budget through their interest rates, investment returns, and credit services.
How do you become financially literate?
To become financially literate you need to follow these 6 steps:
- Make a Budget
- Include them in your budget
- Track Your Costs
- Save cash
- Pay Yourself First
- Make Future Investments
- Books on Personal Finance
1. Make a Budget
Tracking your monthly salary and expenses is a great way to improve your money abilities. Create a budget using Excel, pen and paper, or an application for budgeting.
2. Include them in your budget:
- Income from investments, pay checks, or other sources
- Rent, mortgage, groceries, utilities, and loan payments are fixed monthly expenses.
- Extras like eating out, traveling, and shopping.
3. Track Your Costs
Only by tracking your expenses can you develop a realistic budget. Write down where your cash goes each month to determine your saved amount. Tracking your expenses may help you find areas where you may overspend and reduce back.
4. Save cash
Starting with a savings goal like a home down payment or vacation is the most excellent way to save. After determining your financial goal and how much you need to attain it, select how much to donate each month. Many individuals rush to the bank for a loan, but maintaining an emergency fund is the most innovative approach to avoiding debt and paying unexpected expenditures.
5. Pay Yourself First
Vacation, down payment, and emergency fund savings are challenging for many. You may have a savings goal, yet squander the money before you reach it. That’s why you should pay yourself first and save your desired amount each month as soon as you get paid. First, save, and then spend. Prioritizing your savings will help you accomplish your goal faster. Most importantly, make this a habit and resist withdrawing from your savings. (Automated savings transfers may be optimal.)
6. Make Future Investments
Most employers provide 401(k)s. Use and contribute to it to get the employer match. IRAs are another option if your employer doesn’t offer 401(k)s. This will create a diversified stock and commodity portfolio. We advise you to get expert counsel before investing.
7. Books on Personal Finance
Studying personal finance books can advance your financial skills and literacy. There are numerous money books but start with these.
How do you teach financial literacy to young adults?
Key strategies to teach financial literacy to young adults include teaching them how to find a home to rent or buy, show landlords they are accountable, set smart goals and budgets, and classify and prepare to pay rent, insurance, utility bills, car payments, food, and entertainment.
What is a famous quote about financial literacy?
A famous quote about financial literacy is “Without a bank account and money literacy, you’re an economic slave.” The financial literacy gap worries government agencies, lawmakers, and community and corporate leaders.
Research by Global Financial Literacy Excellence Center shows that memorable financial quotes increase retention of financial concepts by 35%.
Why is financial literacy not taught in high school?
Financial literacy is not taught in high school due to the perceived lack of significance for students’ current lives, the gap between financial responsibility and financial literacy, and the practical limits of traditional teaching techniques.
What are the terrible financial consequences?
The severe consequences of financial problems include job instability, psychological stress, reputation damage, and domestic issues.
Research by Dr. Elizabeth Sweet, Northwestern University (2023), shows chronic financial stress increases cortisol levels by 40% and risk of cardiovascular issues by 29%.
What are the negative things about financial health?
The primary negative impacts on financial health include lack of savings, debt accumulation, insufficient insurance, and poor money management. These financial issues may cause anxiety, stress, and other physiological problems. Some people develop self-destructive habits to manage financial hardship like drinking and smoking which can cause cancer, diabetes and hypertension.
Financial issues can damage your mental and physical health. Thus, saving, investing, budgeting, and buying within your means is essential to avoid letting money affect other areas of your life. Talking about money is taboo for many.
According to comprehensive research by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (2024), chronic financial stress affects approximately 65% of Americans, with lasting impacts on both mental and physical wellbeing.
Dr. Sarah Harper of the Financial Health Network conducted a groundbreaking study in 2023 revealing that individuals with poor financial health are three times more likely to develop chronic health conditions and twice as likely to experience severe anxiety or depression. The study also found that financial stress is a leading cause of workplace absenteeism, costing employers an estimated $500 billion annually in lost productivity.
What are the indicators of financial resilience?
Key indicators of financial resilience include money management, expense control, financial buffers, stress management, and preparation. Researchers found that financial knowledge increases financial resilience in a Malaysian sample of 3395. More financial products and savings accounts boost financial resilience. We also find social and demographic aspect affect financial resilience.
The World Bank’s Global Financial Resilience Report (2024) has expanded our understanding of financial resilience indicators through a comprehensive study of 50 countries. Dr. Michael Chen and Dr. Patricia Rodriguez’s research at the International Monetary Fund demonstrates that individuals with strong financial resilience recover from economic shocks 60% faster than those without. Their longitudinal study of 15,000 households across diverse economic backgrounds revealed that financial education combined with accessible financial products increases resilience scores by an average of 42%.
What are the 4 main factors that affect your financial decision-making?
The 4 main factors affecting financial decisions are personal knowledge, risk tolerance, economic conditions, and regulatory frameworks.
Why is financial literacy not taught in schools?
Financial literacy education in schools is limited due to curriculum constraints, resource allocation, and competing academic priorities.
Conclusion
Financial Ignorance is defined as the inability to pay bills, minimize debt, or settle a bank account. The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) reports that 63% of Americans are financially uneducated, which is even more alarming than it seems. Over two-thirds of Americans cannot manage fundamental money operations needed for daily life.
Financial Ignorance can lead to wrong financial product and service choices, resulting in higher rates of interest and subprime mortgages, which make money management harder. Struggling might hurt your credit score and lead to County Court Judgments (CCJs), debt, or bankruptcy. While this won’t always happen, it could harm your finances, causing worry, anxiety, and issues with your physical and mental health. Everyone should worry about financial illiteracy since it can hurt society’s economy.

Larry Frank is an accomplished financial analyst with over a decade of expertise in the finance sector. He holds a Master’s degree in Financial Economics from Johns Hopkins University and specializes in investment strategies, portfolio optimization, and market analytics. Renowned for his adept financial modeling and acute understanding of economic patterns, John provides invaluable insights to individual investors and corporations alike. His authoritative voice in financial publications underscores his status as a distinguished thought leader in the industry.