Beta is a statistical measure of stock prices’ volatility compared to the market. It shows how much a security’s price will move with the market. For instance, a beta of 1.0 tells the security’s price will follow the market. A beta below 1.0 tells the security will be more stable than the market, while above 1.0 indicates more unpredictable.
Calculation: Beta is derived by regression. This statistical method estimates the link between market returns and stock returns. The beta formula is:
Beta = Covariance / Variance
Covariance: (Return of the security, Return of the market)
Variance: (Return of the market)
Smart beta strategies target factors or investment themes that have historically outperformed market-cap-weighted indexes in risk-adjusted returns. They capitalize on market inefficiencies and improve portfolio performance by not weighing companies by market value.
A publicly traded security’s levered beta evaluates its market sensitivity. Debt is included in a company’s levered beta sensitivity. Assurance with a positive levered beta correlates positively with market performance, while security with a negative beta correlates negatively. A levered beta above or below 1 indicates more volatility than the market. The market is more volatile than a levered beta between -1 and 1.
Due to debt’s tax benefits, unlevered beta is near to zero and more predictable than levered beta. Unlevered beta evaluates a security’s unpredictability and market performance without debt concerns. Due to debt, a security’s unlevered beta is lower than its levered beta, making it a better indicator of market volatility and performance.
The advantage of using Beta is that it aids portfolio diversification. Without collecting and evaluating historical data for each investment, utilizing industry averages for beta saves time and money. It also provides a constant and consistent benchmark for investments in a similar industry because it reflects the typical risk profile. Use industry averages for the beta to balance out noise and instability that can impact individual investment beta estimations, especially if they have a short or inconsistent trading history.
Beta’s disadvantage is that it measures previous volatility and does not predict future performance.Beta based on industry averages cannot convey each investment’s distinctive features and risk concerns. For Example, some investments can have different development prospects, capital structures, competitive advantages, or macroeconomic risk than the sector average. These factors can cause the investment’s beta to differ from the industry average. Industry norms for beta can not reflect actual or predicted circumstances and trends due to the industry and the market’s unpredictable nature.
Boost your portfolio’s growth potential with Beta investing. CapitalizeThings.com offers expert consultations to navigate this strategy.
What is beta investing?
Beta investing is a strategy that aims to match the performance of a specific market index or benchmark, typically through passive investment in index funds or ETFs. Beta measures market risk and volatility. Beta does not mean fraternities, product testing, or obsolete videocassettes in investment. It shows how much a stock’s price fluctuates compared to others. The S&P 500 Index, like every stock index, fluctuates. The trading day ends with the markets moving up or down. Investors considering a stock can want to see if it fluctuates as much as other equities. It can maintain its value on a terrible day or stall when most stocks rise.
The beta number indicates to investors how that stock performs compared to all other equities or an index. Beta measures a stock’s price volatility relative to the stock market. It measures the stock’s risk relative to the market. Beta compares a stock’s risk to the market to others. The Greek letter sign on Beta shows beta to analysts.
Beta: friend or foe for your portfolio? CapitalizeThings.com (+1 (323) 456-9123) clarifies Beta investing & tailors it to your goals. Reach out to us for Free consultation today.
What is smart beta investing?
Smart beta investment techniques use index construction rules other than market capitalization-based indices. They transparently and rules-basely capture investing characteristics and market inefficiencies. Smart beta is becoming more popular as investors seek factor diversification, portfolio risk management, and returns adjusted for risk above cap-weighted indices.
Smart beta strategies passively follow indexes while considering volatility, quality, value, liquidity, size, and momentum. That’s why they utilize transparent index rules like traditional index strategies. These funds concentrate on market opportunities rather than typical indices like the Nasdaq 100 Index or S&P 500.
Is smart beta worth it?
Yes! Smart beta is worthy. Most stock market indexes are capitalization-weighted, making smart beta effective. This means they rank index stocks by market cap. Market capitalization is usually a good predictor of market health, but it doesn’t always predict growth. Smart beta funds exploit this. They intend to maintain market index stability while adding profitable assets.
What is the best performing smart beta ETF?
VanEck Morningstar Wide Moat is the best performing smart beta ETF. The smart beta ETF MOAT has outperformed the S&P 500 since its introduction with 13.7% versus 12.6%. MOAT’s strategy relies on Morningstar’s quantitative technique to find cheap businesses with a wide moat or sustained competitive advantage. Morningstar says this advantage comes from intangible assets, a cost advantage, scale, high switching costs, and a strong network impact. MOAT also filters for reasonable prices to prevent the ETF from overspending for wide-moat stocks. MOAT expenses are 0.46%.
What is beta in finance for dummies?
Beta (B) in finance for dummies measures a securities or portfolio’s volatility, or risk profile compared to the market. The capital asset pricing model (CAPM) depends on it to evaluate asset risk and expected return. Estimating a stock’s risk in a diverse portfolio while investing is crucial. This is where beta helps. Beta shows stock volatility when compared to the market. The S&P 500, with a beta of 1.0, is used to calculate beta. Betas above 1.0 tend to be more unpredictable than the market, while betas under 1.0 are less volatile.
What is a good beta in investing?
A good beta in investing is higher than 1.0.
What is Levered beta and unlevered beta?
Levered beta is affected by leverage, which indicates a business’s debt to equity. According to levered beta, a company with a combination of debt capital and equity structure is risky to market volatility. Another beta is unlevered. Unlevered beta eliminates the benefits and drawbacks of debt in the firm’s capital structure. Compare firms’ unlevered betas to understand the risk of buying the stock.
What is the meaning of beta in investing?
The Greek letter beta is used in finance to indicate the volatility or regular risk of a portfolio or security relative to the market. For example, the S&P 500 carries a beta of 1.0. Betas above 1.0 indicate more volatility than the S&P 500.
What is the connection between beta and CAPM?
Beta is CAPM’s standard systematic risk measure. It measures the tendency of a security’s return to track the stock market. Beta estimates the volatility of a security relative to the market. An average-risk stock with a beta of 1.00 fluctuates in value at the same rate as a broad market index like Standard & Poor’s 500-stock index. Stocks with betas above 1.00 are risky and market-sensitive. Stocks with a beta below 1.00 have low systematic risk and are more resistant to market swings.
What is the beta coefficient theory?
The beta coefficient in finance predicts the ups and downs of a stock price relative to the overall stock market. Beta measures the overall risk of a portfolio when a modest amount of an asset is added. An asset’s systematic, non-diversifiable, or market risk. Beta does not indicate individual risk.
What is a beta investment strategy?
A beta investment strategy aims to match the performance of a market index by replicating its composition and returns. Your conditions and aims should guide your alpha or beta strategy choice. Copper’s cost curve helps explain resource industry alpha and beta tactics. The cost curve can assist investors in finding mines with positive alpha and market outperformance.
How is beta helpful for investors?
Beta helps investors to compare a company to a market-tracking index fund but doesn’t fully assess risk. Instead, it measures its volatility, which might be beneficial or harmful. Investors don’t mind rising prices. The price drop will keep folks awake at night. Compare stock betas like you would order cuisine at a restaurant. As a risk-averse investor focused on income, you can avoid high-beta stocks, as a simple eater might pick a plain dish with recognized components and flavours. An ambitious investor with greater risk tolerance can chase high-beta companies like an adventurous eater who seeks fresh, spicy dishes with novel ingredients.
How do you calculate beta?
Beta is calculated by dividing the covariance of an asset’s returns with the market’s returns by the variance of the market’s returns. Covariance measures a stock’s return relative to the market, whereas variance measures the market’s movement compared to its mean. Once those statistics are found, covariance divided by variance yields beta.
Beta = Covariance/Variance.
How do you read the stock beta?
Reading a stock beta involves following:
- A beta greater than 1 shows a stock’s price instability is higher than the market.
- Less than 1 beta means a stock’s price is less unstable than the market.
- A beta of 1 tells the stock moves like the market.
How do we determine if the value of beta is good or bad?
To determine if the value of beta is good or bad, read the following:
- Beta Equal to 1: A beta of 1 means the security’s price moves with the market.
- Beta Less than 1: Security prices above 1 are more unpredictable than the market.
- Beta Greater than 1: With a beta below 1, it is less volatile than the market.
- Negative Beta: An investment with a negative beta rises as the market drops and vice versa. Securities borrowing is a negative beta investment. Due to falling market returns, rates of lending rise.
What does a beta of 1.3 mean?
Having a beta of 1.3 makes an asset 30% more unpredictable than the market. Stocks have strong betas since they’re market-correlated. Stock beta indicates how much its price moves about the market. Stocks with betas exceeding 1 are more unstable than the market.
How do you calculate levered beta?
To calculate levered beta, multiply unlevered beta by 1. The result is the product of (1—tax rate) and the company’s debt-to-equity ratio.

Financial databases like Reuters and Yahoo Finance are used to report a company’s levered beta.
How to calculate beta for a portfolio?
Each stock, asset, or holding’s beta is averaged to calculate portfolio beta.
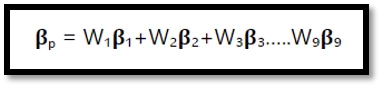
B = beta of the holding
bp = beta of the portfolio
W = holding weight (relative to your portfolio).
What are the examples of beta stocks?
Beta changes with time and market circumstances. It ignores intrinsic value and company strength, which determine stock risk and return. Beta alone shouldn’t be employed to assess a stock’s risk. Use it with fundamental and technical analytical tools. Searching online or utilizing a stock screener to filter for companies with a beta greater than 1 will yield a thorough list of high-beta equities. Before investing, do your research and contact a financial expert.
Examples:
High Beta: A corporation with a beta greater than 1 is more erratic than the overall market. A high-risk technology business with a beta(B) of 1.75 should have returned 175% of the market return in a particular period (typically measured weekly).
Low Beta: A corporation with a beta below 1 is less risky than the market. Consider an electric utility corporation with a beta of 0.45, likely generating only 45% of the overall market return over time.
The video below can help you with understanding the example of beta.
What is an example of a smart beta strategy?
Let’s look at the example of a smart beta strategy, A business creates an S&P 500 smart beta ETF. It might first fill the fund with S&P 500 stocks or others that closely match that index. The fund will next set its higher-return criteria. For instance, the fund can own smaller stocks with growth potential. In an S&P 500 index fund, these equities could boost returns over the market average.
Because most equity indexes are capitalization-weighted, smart beta works well. They prioritize index stocks by market cap. That usually indicates market health. However, market capitalization only sometimes predicts growth. Smart beta funds capitalize on this. While adding profitable assets, they strive to maintain market index stability.
What are the Pros and Cons of using Beta in Finance?
The pros and cons of using beta in finance are given in table below:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Beta indicates whether a stock will fluctuate more or less than the overall market as a percentage. | Beta varies: Betas alter when stocks and markets change and economic and financial circumstances fluctuate. They also change throughout time. |
| Beta helps you manage portfolio volatility and adapt to market changes. | Unreliable for short-term predictions: Statistics also improve over time. Beta is especially error-prone for short-term estimates like days or weeks. Every trading day, a stock with a beta >1.0 won’t be more volatile than the market. |
| Beta is easy to comprehend, and a large amount is available. |
What are the risks of smart beta ETF?
Risks of smart beta ETF are:
- Smart beta ETFs are more complicated than market-cap-weighted indexes, which can perplex investors.
- Compared to index funds and actively managed mutual funds, smart beta ETFs have a short track record, making long-term evaluation difficult.
- Smart beta ETFs can leave from their index or investing aim, causing tracking errors.
What is market risk beta?
Market risk beta measures a security’s sensitivity to market movements, indicating how much its returns fluctuate relative to overall market returns.
Market risk got you down? CapitalizeThings.com (+1 (323) 456-9123) uses beta to guide you towards a less volatile portfolio. Get a free 15-minute consultation by emailing us.
What is the beta of systematic risk?
Stock market investing involves systematic risk, which impacts a whole market or an extensive section. Beta measures systematic risk by comparing stock volatility to the market. An investment with one beta has the same risk profile as the stock market. Beta assesses market risk’s effect on stock returns.
What is beta in investment banking?
Beta in investment banking measures a stock’s volatility relative to the overall market, indicating how much its price moves compared to a benchmark index. The beta(B) measures a stock or portfolio’s market risk or unpredictability. It estimates a stock’s portfolio risk. The S&P 500 is beta 1.0.
Does beta investing influence investment banking strategies?
Yes! Beta investing influences investment banking strategies.
How does investment banking assess beta investing returns?
Investment banking assesses beta investing returns by measuring a portfolio’s performance relative to market risk (beta) to determine how much returns are attributable to overall market movements. Beta is computed by dividing the multiplication of the security’s covariance and the market’s returns by the market’s variance during a set period. The calculation tells investors if a stock follows the market and shows how volatile or hazardous a stock is compared to the market.
What is a stock beta for dummies?
Stock beta measures a stock’s volatility compared to the overall market, a beta of 1 means an investment moves in pace with the market, while beta larger than 1 means higher volatility and beta less than 1 means reduced volatility. Investors need this statistic to assess investment risk and portfolio diversity.
What is the end goal of using the beta strategy in Investing?
The end goal of using the beta strategy in investing is to manage risk by comparing a portfolio’s volatility to the market, aiming to achieve returns that match or exceed the market with controlled risk exposure. Smart beta strategies invest in adapted indexes or ETFs, depending on one or more factors, to enhance returns, diversify, and decrease risk. Their goal is to outperform capitalization-weighted benchmarks with lower risk and expenses than actively managed funds.
What is a high beta index?
High beta indexes comprise stocks with higher volatility than the general stock market. Examples are the S&P 500, TSX Combination, Hang Seng, and S&P Emerging Markets High Beta Indexes.
How does the expected return vary with the beta?
The expected return increases with higher beta, as beta measures the stock’s risk relative to the market, and higher risk demands higher returns according to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM). A stock with a beta of 1.5 indicates 150% of the market average instability. If the beta is 1, a security’s predicted return equals the average market return.
Is a beta the same as a return?
No! It is the part of return.Beta measures market risk, and diversity cannot lower it. It is the market’s share of portfolio return, not the fund manager’s or shareholders’ skill.
What does a 100% beta mean?
A 100% beta is impossible because it suggests 100 times market volatility. A stock with a beta of 100 would fall to 0 on a market drop. Betas over 100 on research sites are usually statistical errors, or the stock has had a spectacular and perhaps deadly price fluctuation. Established company stocks rarely have a beta above 4.
What is a good Beta for a portfolio?
A good portfolio beta is 1.0. Beta measures risk-reward and portfolio sensitivity to market fluctuations. The market benchmark index is 1.0; therefore, investors should strive to stay close to it to achieve the lowest volatility in their portfolios.
What does a beta of 0.9 mean?
In rising markets, a fund with a beta of 0.9 will perform 10% worse than the index but 10% better in down markets. If the index increases by 10%, the fund should gain 9%. A 10% market drop would reduce the fund’s value by 9%.
What does a beta of 0.8 mean?
A beta of 0.8 makes a corporation 80% as unpredictable as the market index. The stock is 20% more stable than the market.
Is a 1.3 beta good?
Yes! It will be good for you if you are an excellent risk-taker.
What is the difference between alpha and beta investing?
Beta estimates volatility compared to a benchmark. It compares a securities or portfolio’s systematic risk to the S&P 500. The beta of many growth stocks is likely significantly higher than 1. Treasury bill prices move little compared to the market; hence, their beta is near zero.
Beta is considered a multiplication factor. A 2X leveraged S&P 500 ETFs beta is close to two by design. It fluctuates twice as much as the index. The majority of negative beta investments are inverse ETFs or Treasury bonds.
Alpha is an investment’s extra profit after market downturns and random changes. Alpha is one of five primary mutual fund, stock, and bond risk management indicators. It shows investors if a stock has consistently outperformed its beta. Alpha measures risk. The investment was too risky for a return with an alpha of -15. Zero alphas mean an asset’s return matches its risk. After volatility adjustment, an investment with a higher alpha outperformed.
Is the beta investing strategy linked to S&P 500 performances?
Yes, the beta investing strategy is linked to S&P 500 performance, as beta measures a stock’s volatility relative to the market, often benchmarked against the S&P 500. It ignores firm fundamentals, profitability, and growth potential.
Can SIP strategies be optimized using beta investing?
Yes, SIP strategies can be optimized using beta investing by selecting funds with appropriate beta values to align with desired risk levels and market volatility exposure.
Does beta investing enhance investment management strategies?
Yes! Beta investing enhances investment management strategies. Smart beta techniques increase returns, diversify, and minimize risk with variable-based indexes or ETFs. They aim to outperform capitalization-weighted benchmarks with lower risk and lower expenses than actively managed funds.
Does mastering beta investing enhance investment skills?
Yes! Mastering beta investing enhances investment skills.
Does beta investing influence investment tax strategies?
Yes! Beta investing influences investment tax strategies.
Does beta investing simplify investment choices for beginner investors?
Yes! Beta investing simplifies investment choices for beginner investors. Individuals who can’t take risks will invest at a low beta.
Can shareholders benefit from beta investing strategies?
Yes! Shareholders benefit from beta investing strategies. Investors can design a risk-appropriate portfolio by understanding stock beta. Recently, investors have used smart beta index investing. An advanced indexing approach called smart beta exploits performance characteristics that beat a benchmark index. Thus, smart beta varies from passive indexing.
Does beta investing incorporate ESG criteria?
Yes! Beta investing incorporates ESG criteria. Smart beta portfolios weight ESG aspects and scores to boost risk-adjusted returns, lower downside risk, and enhance ESG risk.
Does beta investing affect the P/E ratio of stocks?
No! Beta investing does not affect the stock’s P/E ratio. When evaluating companies in a sector, the PE ratio indicates shareholder expectations for future growth. The CAPM formula states that shareholders need a more significant return for increasing betas and risk.
Is there a correlation between beta investing performance and the PB ratio?
No! There is no correlation between beta investing performance and the PB ratio.
Conclusion
Beta is essential for risk assessment and investment decision-making in finance. Its significance, estimation, and use help investors design portfolios that match their risk taking ability and financial goals. Learning beta is essential for investors of all levels as they navigate the complex markets of finance. Finance uses beta to compare a securities or portfolio’s volatility to the market. It’s crucial to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), which calculates asset returns.
Market risk is measured by levered beta (equity beta). Company risk is calculated using debt and equity. Unlevered beta isolates corporate asset risk from debt.
The advantage of Beta is that investors and analysts use it to assess stock risk. Beta can be combined with alpha to make investing decisions. Beta is simple to calculate and comprehend. Disadvantage of beta is that it alone should not be used to assess risk. It readings can fluctuate, thus they must be monitored. Beta is subject to market conditions and can be inaccurate.

Larry Frank is an accomplished financial analyst with over a decade of expertise in the finance sector. He holds a Master’s degree in Financial Economics from Johns Hopkins University and specializes in investment strategies, portfolio optimization, and market analytics. Renowned for his adept financial modeling and acute understanding of economic patterns, John provides invaluable insights to individual investors and corporations alike. His authoritative voice in financial publications underscores his status as a distinguished thought leader in the industry.