Investment banking provides capital to other firms and enterprises. Issuers use investment banking for stock placement. Investment firm employees must have specific abilities to manage the complicated and fast-paced World of finance. Whether you’re a professional or just starting out, developing and perfecting key abilities will boost your chances of success. Analytical skills involve finding patterns and drawing conclusions from data. Investment professionals analyze financial data, model data, and determine which investments best meet a firm or client’s goals. This analytical skill requires statistical knowledge and data visualization skills. Attend professional instruction and master your tools and applications.
Effective communication matters. Investing professionals manage others’ money. Businesses need to communicate regularly and effectively to update clients on their portfolios. Confidence and reputation are built on transparency and honesty. To improve this skill, watch your tone, remember that small conversation pays off, be aware of your nonverbal clues, and find common ground. Investment experts process lots of data daily. Critical thinking is needed to make sense of so much data. To succeed in this career, you must observe, evaluate, and draw inferences from facts to construct a comprehensive picture before making a judgment call. The top 24 skills to learn before investing are:

1.Analytic reasoning
Critical thinking-based analytical reasoning helps to answer complex questions with logic while we look to invest. Patterns in information or rules can be used to discern true or false results. The analytic hierarchy technique helps characterize investors by investing suitability. The methodology makes security selection less subjective without compromising the broker’s capacity to customize portfolios. Formal security selection models generate more consistent outcomes. They insulate brokerage and trading companies from unsuitability litigation (Determining Investor Suitability Using the Analytic Hierarchy Process, P. Bolster, Vahan Janjigian, E. Trahan, 1995).
You need to identify multiple analytical reasoning features to conclude, such as:
Causation: Understanding that one occurrence caused another, rather than correlation, where two events occurred together but were unrelated.
Conditional statements: Conditionals, or ‘if-then’ statements, state a hypothesis and an inference. A converse statement switches the conclusion and hypothesis.
Trends: Quantitative, precise statistics can show when an outcome continuously increases or declines. This is trending.
Sequences: Finding the pattern or rule that makes a seemingly unrelated set of numbers, images, or shapes a sequence can assist you predicts the next.
2.Communication
Communication skills are used to receive and give information. Examples include sharing pristine thoughts of business investments, sentiments, or project updates. Listening, speaking, watching, and empathizing are communication skills. Understanding how phone calls, email, and social media differ from face-to-face interactions is also helpful. To enhance your communication skills, you can practice several communication skills. Many of these abilities operate together, so practice communication in multiple circumstances whenever feasible.
- Responsiveness
Fast communicators are more effective when answering calls or responding to emails. One way is to estimate response time. Is this request or question within five minutes? It can be best to handle it immediately. If it’s a complicated request or query, you can confirm receipt and promise to react later.
- Non-verbal cues
Non-verbal messages are normally sent through jargon, body language, and eye contact. Listen to what someone says and their nonverbal cues. Watching your body language when conversing can help transmit the right cues.
- Respect
Respect involves understanding when to speak and reply. Allowing others to talk uninterrupted is a team communication ability. Respectful communication entails staying on the subject matter, asking straightforward questions, and answering questions thoroughly.
- Empathy
Empathy implies understanding and sharing another’ feelings. This communication skill is crucial in teams and one-on-ones. In all circumstances, you must comprehend others’ emotions and respond appropriately. Empathy can help you understand and calm someone’s rage or fury. However, recognizing positivity and enthusiasm might help you gain support for your ideas and objectives.
- Confidence
Confident ideas are more likely to be accepted at work. Making eye contact, sitting up tall with your shoulders open, and rehearsing your thoughts ahead of time will help you appear confident. Confident communication helps on the job and in interviews.
- Active listening
Active listening involves paying deep attention to the speaker. Co-workers respect active listeners for their attention and respect. It looks easy, yet this ability is difficult to master. Active listening requires concentrating on the speaker, minimizing distractions such as cell phones, computers, and other work, and preparing insightful questions, remarks, and ideas to answer.
3.Financial analysis
For efficiency and feasibility, financial analysis assesses businesses, budgets, projects, and other financial transactions. It also assesses whether a company is stable, liquid, solvent, or profitable enough to merit investment. Financial analysis should objectively estimate a company’s overall market value, excluding emotions and allowing ongoing arbitrage between market and substitute value (Investment, investors, and financial analysis, P. Costantini, 2006).
Financial numbers and data are synthesized. A financial analyst will analyze a company’s balance, income, and cash flow statements. Investment and corporate finance involve financial analysis. A typical technique to assess financial data is to derive ratios from financial statements and compare them with other companies or the company’s previous performance. The return on assets (ROA) ratio is used to quantify a company’s profitability and asset efficiency. A more comprehensive investigation could compare this ratio for multiple companies in the same industry.
4.Risk management
Risk management involves recognizing, assessing, and managing financial, legal, tactical, and security threats to assets and earnings. Economic uncertainties, legal liability, strategic management failures, accidents, and natural disasters might pose these risks. A minimal impact on overhead costs can result from an unexpected incident catching your business off guard. Unfortunately, it could be disastrous and lead to financial hardship or the sale of your business. An organization must allocate resources to avoid, monitor, and regulate unfavorable events and maximize positive events to lower risk. A systemic, systematic, and integrated risk management strategy can assist in identifying, managing, and reducing significant risks.
Risk management is a staff, procedures, and technology system that helps organizations set values and risk-based goals. A successful risk evaluation program must meet legal, contractual, organizational, social, and ethical goals and monitor new technology laws. By focusing on risk and allocating resources to regulate and mitigate it, a firm reduces uncertainty and costs and improves continuity and success. Risk identification, evaluation, reduction, and monitoring are crucial to risk management.
- Recognizing risks
Risk identification involves assessing hazards to a business, its operations, and its employees. Risk identification include examining IT security threats like malware and ransomware, natural catastrophes, accidents, and other occurrences that could interrupt corporate operations.
- Analysis and risk assessment
Risk analysis determines the likelihood and result of risk events. Risk appraisal assesses risk magnitude and ranks them by importance and impact.
- Mitigating and monitoring risk
Risk reduction involves planning and developing ways to lessen project risks. A project team use risk mitigation tactics to identify, monitor, and assess project risks and repercussions, such as fresh product creation. Risk mitigation addresses project difficulties and their repercussions. Risk management evolves continuously. Monitoring and Repeating processes can enhance risk coverage for known and unknown threats.
5.Discipline
Discipline is training people to follow the rules and behaviors of a company or a business. Self-discipline is similar, except we suite ourselves to regulate our behavior, thoughts, and body. Training in discipline frequently involves obedience, strict rules, and punishment. Unfortunately, this disciplinary feature makes us harshly assess our acts. Developing self-discipline doesn’t mean hating oneself, and it doesn’t mean ignoring self-compassion. Self-imposed threats and punishments don’t teach discipline.
Self-discipline is a soft talent that can be used in many contexts, and traders always look for it and need it themselves for their business growth. Like quitting a harmful habit, emotional self-regulation requires regular effort. This is similar to self-management, which involves taking responsibility for your actions and their rewards or consequences. It’s impossible to enhance self-discipline without improving willpower. Your will, or “willpower,” is an inbuilt response that allows you to push yourself to continue, whereas self-discipline involves constraint and control. Resisting chocolate cravings requires willpower, but not buying chocolate is about discipline and anticipating future challenges.
Self-discipline is essential to developing other talents, including tenacity, resilience, dedication, stamina, self-confidence, self-motivation, rigor, organization, autonomy, and more. Thus, it is the key to success. The good news is that practice perfects this skill. Daily practice till it becomes automatic.
Self-discipline predicts success better than IQ. Psychologists like Angela Duckworth found that self-disciplined persons are likelier to stick to their long-term goals despite setbacks. Maintaining long-term motivation requires self-discipline. Long-term maintenance of new habits like sports or healthy eating is challenging. Studies demonstrate that going for a run or refusing chocolate becomes automatic once you form a new habit.
Self-disciplined people are more likely to stick to new behaviors. In 2013, a study found that they were satisfied than others. According to the survey, self-disciplined people avoided unhealthy behaviors without second-guessing their choices. After weighing the merits and cons, they chose positive behavior and stayed to it without being affected by their emotions or wishes.
6.Innovation
From developing a machine to discovering a faster way to operate, innovation creates value and improves operations. Innovation skills help you solve difficulties and learn more at work. Developing innovative abilities will help you land top jobs and advance your career. This post discusses innovative talents and how to apply them to advance your career. Innovating and adapting requires knowledge and skills. They help you generate new ideas for your team using your present knowledge. Innovative people see things from numerous angles and critically evaluate the best solution. Strong work innovation skills require personal traits, interpersonal intelligence, and technological expertise to advance your career. Investor sentiment, equities valuation, and IPO markets rise during innovation waves due to underlying uncertainty, not misperceptions (Uncertainty, Investor Sentiment, and Innovation, David L. Dicks, P. Fulghieri, 2020).
Innovative people can utilize their imagination to find better ways to do things. Strong imagination lets you forecast the result of your ideas and find inventive solutions to attain your goals. Imagination can help you and your team brainstorm, invent, and advance your field. Innovative people use difficulties to improve processes or generate new products. Innovation involves identifying common issues and discovering solutions. Problem-solving skills save money, boost efficiency, and resolve client difficulties at work. Innovation involves fresh ideas and reasonable implementation standards. Innovative ideas are realized through product and process design. Technical design abilities like product creation and engineering can create working prototypes.
7.Leadership
Leadership skills enable people to manage procedures, lead initiatives, and motivate employees of a company. Leadership abilities help leaders make intelligent judgments about their organization’s vision and goals and deploy resources to achieve them. Delegation, inspiration, and communication are valuable leadership characteristics. Other leadership attributes are honesty, confidence, devotion, and innovation. Often, IT leaders must be multitaskers. They must lead in compliance, disaster recovery, risk control, data governance, and strategic planning.
A leader needs specific qualities to guide and motivate team members to succeed. A strong leader communicates with team members through one-on-one sessions, email, video, chat, phone conversations, and social media to convey organizational goals and tasks. Influential leaders communicate clearly and simplify complicated topics for everyone. Empathetic leadership involves empathizing and understanding people. Empathetic leaders succeed because they know how employees feel about their workplace. This lets leaders improve the workforce. Leaders must make difficult decisions that require strategic and critical thought. Strong leaders make well-researched, objective decisions that help an organization achieve its goals. A good leader would always reward employees for their creativity.
8.Portfolio management
Financial professionals who invest others’ money are called portfolio managers. They analyze economic data and market situations and invest accordingly. Hard and soft portfolio management abilities can boost your work prospects and performance. Portfolio managers have soft and hard skills. Soft skills like communication, teamwork and leadership are vital for client management and teamwork. Hard skills, like risk management, financial analysis, and investing techniques, are needed to construct and manage a portfolio.
Portfolio managers interact with many persons and entities. It would help if you properly communicated investing strategy, market conditions, and risk assessments. You must listen and communicate to comprehend your client’s and team’s requirements and goals. Portfolio management success typically hinges on teamwork. Thus, working well with others, understanding their strengths and shortcomings, and negotiating disputes constructively is crucial. Portfolio management requires tough decisions in unstable markets. Under pressure, you must evaluate multiple perspectives and choose the best course of action based on logic and evidence.
9.Detail-oriented
Detail-oriented people pay attention to every detail and finish each assignment before moving on to next task. You produce high-quality, error-free work. Paying attention to details offers unlimited workplace rewards. Precision shows commitment and professionalism, resulting in high-quality work that is required to deliver in a business. Most businesses like carefully focused workers, so these abilities give you an edge.
Detail-oriented talents involve focused attention to and management of a task or project’s details. Organization, compassion, and attention protect you from missing essential facts. These talents let you spot even the smallest details, ensuring your project is perfect. Mastering detail-oriented activities at work helps you avoid mistakes and produce high-quality work.
10.Private Equity
Private equity is a challenging yet rewarding career. Start a private equity (PE) career with excellent networking and analytical abilities. Private equity invests in private organization or acquires public corporations with investor capital. Doing so gives general partners power over management and other operational improvements to boost profitability and sell successfully. Smaller than investment banks, private equity businesses can have 5–10 employees.
Several significant private equity firms with large market caps are emerging. Whatever the size, these businesses’ associates deploy private equity capital for portfolio companies in all industries and stages of life. Investment firms or wealthy individuals raise private equity funds. Funds buy and delist the outstanding shares of private or faltering public corporations. After buying portfolio companies, PE firms engage with management to streamline operations to decrease costs and inefficiency. Private equity firms hang onto their investments for 10+ years before selling for a profit, opposing hedge funds.
As mentioned, private equity careers are competitive and demand relevant experience and strong abilities. Private equity specialists work long hours, are competitive, and must think critically and love financial investing opportunities, not simply markets.
Other prerequisites for private equity skills include:
Grades and transcript are outstanding. An MBA or advanced degree is helpful but optional. Previous experience is typically required & encouraged. PE firms are competitive; thus, good networking skills are helpful when applying. Requirements include strong problem-solving and analytical skills, expertise in bolt-on acquisition analysis, market studies, CIM evaluations, financial modeling, and LBO creation for client deals. An internship in a private equity firm or a similar industry like investment banking or consulting for management would help you understand the environment. PE firms prefer forceful, independent, and analytical candidates.
11.Time management
Time management coordinates duties to maximize an individual’s efforts. Time management helps people achieve more and greater success in less time. Time management involves organizing, planning, and scheduling to optimize time. Time management methods also consider an individual’s situation, skills, and traits.
Effective time management is crucial. Good time management boosts productivity of a person that helps the company to achieve its goals and it reduces stress and boosts success. Effective time management has many benefits:
Regular task scheduling decreases anxiety. You can see progress as you cross off tasks on your “to-do” list, preventing you from worrying about getting things done. Good time management frees up daily life. Time-management experts enjoy extra time for hobbies and other interests. Better time management means more opportunities and less time spent on unimportant things. Employers value time management. Any company wants to prioritize and schedule tasks. Good time management helps people reach goals faster.
Time limits help you focus and work efficiently. Being extra careful about how much time you need for each work lets you spot possible issues. This enables you to plan for them. Say you have five points to write for a meeting. You know you can only finish four of them before the meeting. Knowing this ahead of time allow you to delegate review writing. If you hadn’t checked your tasks’ time beforehand, you would only get to know your problem an hour before the meeting. At that point, it can take more work to find someone to assign a review to and fit it into their schedule. Staying motivated and focused is tougher when working nonstop. Break between chores to recharge and clear your mind. Try a short nap, walk, or meditation.
12.Analysis
Analysing the business operations is a main task,so throughout your job hunt, you should list technical and interpersonal abilities on your CV and other application materials. Through reflection and experience, you can enhance your analytical thinking, a soft skill valued by many organizations. Enhancing your analytical abilities allows you to achieve your career goals and be happy.
Analytical talents enable you to observe, research, and interpret a topic to find complex answers. Combining these talents is analytical thinking. Many professional and personal circumstances can benefit from analytical thinking. Experimentation and other methodical techniques help analytical thinkers obtain logical conclusions. Practical analysts can swiftly understand a scenario, topic, or problem and function well in teams to achieve goals.
Data management and IT require analytical skills, which are useful in numerous fields and professional levels. Strong analytical skills can improve a company’s operations, so employers respect them. A customer care lead with excellent analytical abilities evaluate refund data and discover trends to help the team reduce refunds. These talents demonstrate your worth to the firm and can qualify you for a leadership role or promotion.
4 skills for good analysis are the following:
Problem-solving
After researching an issue, use your creative problem-solving talents to create a solution. You could test your solution or get feedback. Leisure center management can use surveys to learn what exercise classes members like and when they want to take them. They might then use their problem-solving talents to match classes with qualified teachers. Finally, they can change the course timetable with comments.
Research
The ability to conduct research can assist you determine the most efficient solution to a problem. The research process might involve asking experienced co-workers for their insight into a problem or conducting formal research into external sources. You could also plan study experiments to test various goods or marketing strategies, depending on the field. Knowing what knowledge is useful or necessary to solve the problem is also part of the research process.
Information and Data analysis
Information and data analysis are critical to analytical thinking. These abilities can help you find problems and solutions by utilizing data and improving decision-making. A café manager can track when and what clients order. The management can use this information to change staffing and prepare for orders, enhancing café efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking allows you to examine preconceived assumptions and find problems or places for growth. Every level of work benefits from this talent since it helps organizations innovate. Innovation frequently begins with critical thought. A logistics company can utilize a stock-organizing system for decades. A fresh operational manager can dispute this system’s purpose. Identifying the company’s demands allows them to change or replace the system.
13.Asset management
Leading asset management companies agree that a manager’s ability to perform well depends on various personal and intellectual skills. Because of this, leaders are being pushed to prepare better and better.
Asset managers today must have sound economic reasoning, comprehensive vision, and knowledge of global macroeconomics & geopolitics. Many financial experts specialize in one country or region but are increasingly asked to assess cross-regional occurrences. Higher oil costs, decreasing US growth, China’s involvement in the global economy, and financial linkages can affect the World. Clients want asset management organizations to analyze these concerns. The 21st-century asset manager archetype stresses math and economics. Employers seek finance enthusiasts and outside-the-box thinkers.
Engineering, arithmetic, and physics experts are employed for multi-asset management, trading, and risk administration roles requiring data and model work. Because they can examine numerous circumstances, non-traditional management companies can recruit people with diverse academic and professional backgrounds because they know they all bring different skills.
The pandemic-caused financial crisis has increased the need for critical thinking; therefore, knowledge management can help. Thus, an asset manager must be well-versed in finance, historical events, political economy, scientific theory, and the arts. The specialist needs tools to examine daily theories and happenings.
14.Due diligence
Due diligence is evaluating, researching, and assessing a decision before making it. Lawyers and analysts do due diligence on significant deals to help clients make informed judgments. Everyone researches while reading reviews or comparing options before buying. Due diligence is hard to identify due to its specialized and daily uses. Due diligence involves critical thinking in daily decisions. If you check a few vacuum cleaner video reviews before buying, you did your research.
Due diligence involves studying, assessing, and avoiding company or investment risks in professional settings, such as finance and business. Before acquiring a firm, a company undertakes due diligence by studying its fiscal history and financial documents. The Securities Act of 1933 made due diligence prevalent in banking and business. Securities salespersons must give prospectuses for each security sold under this act.
You can do due diligence in your daily life by studying and scrutinizing a transaction or choice before committing. If you’re buying a car, investing $100 in the stock market, or picking supper tonight, you perform due diligence by assessing the risks and making informed decisions. Professional due diligence is stricter. Analysts construct checklists for M&A and legal situations. This checklist comprises all due diligence steps, and information analysts will analyze them before reaching a conclusion. Professionals usually acquire data before analyzing it.
15.Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship talents include leadership, business administration, time management, creativity, and problem-solving. Many jobs and sectors use these talents. Entrepreneurship skills boost innovation, growth, and competitiveness. Development of these skills requires various skills. For instance, successful entrepreneurs need to improve their risk-taking and company management skills.
Entrepreneurs need business management abilities to run a company and achieve goals. Entrepreneurs with this skill set can manage multiple departments because they know each function. Business management abilities include multitasking, delegation, and critical decision-making. Entrepreneurs must communicate well with clients, team members, and other stakeholders. Entrepreneurs need excellent written and vocal communication for meetings, reports, and communications. Entrepreneurs need good listening and communication skills to comprehend and discuss project requirements in meetings. A crucial entrepreneurial skill is taking calculated and intelligent risks. Because measured risks lead to great success, entrepreneurs in the workplace never hesitate to take risks. They see danger as a chance to learn and grow a firm. Employers desire applicants who can take risks for profit.
16.Financial knowledge
Financial literacy includes managing personal financial, expenses, and investing. It is vital for wise money management and can start a lifelong financial education. Early financial literacy is superior since education is the key to financial success.
Since 2000, financial services and goods have spread throughout society. Debit and credit card payments and electronic transfers are widespread today, unlike in previous generations when Americans mostly paid cash. The Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco found that 27.99% of payments were generated by credit card and 20% by cash in 2021. Modern civilization relies on finance, so lacking financial literacy can hurt an individual’s economic future.
Financial illiteracy can lead to unmanageable debt due to poor spending or a need of long-term planning. This can cause bad credit, bankruptcy, foreclosure, and other issues. Free learning options are accessible via the Education Commission and US government-sponsored Financial Literacy.
17.Financial statements
Financial reporting is essential for business professionals who want to explain an organization’s financial performance and position. Financial statements and reports must be prepared, analyzed, and presented according to accounting rules. Decision-makers, creditors, investors, and other stakeholders can assess a business’s financial health and prospects via financial reporting.
Accuracy and detail are crucial to financial reporting. Financial statements and declarations must be accurate, thorough, and consistent to reflect the business’s financial realities and affect its reputation, reliability, and compliance. Following accounting standards and processes, checking and verifying data sources, using proper tools and software, and reviewing and proofreading your work will ensure precision and care to detail.
Financial reporting requires critical and analytical thinking. Financial reporting involves understanding and explaining numbers. Financial data must be analyzed and evaluated to find patterns and trends, compare possibilities, and make relevant conclusions and suggestions. You must also be able to critically evaluate financial reporting assumptions, constraints, and risks and question data and methodology.
18.Networking
Networking in businesses entails building mutually advantageous relationships with people (strangers or acquaintances) from similar professional and social networks. To improve networking, you need the necessary abilities. Active listening goes beyond hearing. Pay close attention to the speaker, ask clarifying questions, and ensure you understand the conversation. Communication is the most crucial networking skill. Having wit, insight, talent, and intelligence is only helpful if you can communicate.
Therefore, when networking, be conscious of how you communicate, connect, and address possible concerns and arguments. This involves your tone, language, and haste to talk over others. All of these can break or make your networking. Up to 93% of verbal communication is non-verbal. This includes body language, facial expressions, and position facing your co-speaker. Nonverbal communication is crucial for networking. Communication and interpersonal abilities are sometimes used interchangeably but differ slightly. Interpersonal skills are your capacity to get along with and comprehend others. This normally require being open to subtle cues or “reading” a social situation.
19.Microsoft Office
Microsoft Office 365 skills comprise Word, Excel, Outlook, PowerPoint, Access, Publisher, and Teams. If your employment requires regular Microsoft Office use, add that to your resume. You should also check the job description for Microsoft Office software requirements.
Microsoft Word Skills
- Formatting
- Adding and Reviewing comments
- Tracking changes
- Making bibliographies
- Creating forms and templates
- Creating graphs and charts
- Creating mail merge templates
- Making master documents
- Setting up password protection
- Inserting columns
- Inserting footers and headers
Microsoft Excel
- Creating pivot tables
- Using slicers
- Using advanced functions and formulas
- Conditional formatting
- Working with macros
- Making lists
- Data simulation
- Using sparklines
20.Microsoft PowerPoint
- Creating presentations
- Creating charts
- Designing templates
- Inserting media
- Inserting hyperlinks
- Creating animations
- Using the Accessibility Checker
Microsoft Outlook
- Creating rules
- Organizing inboxes
- Archiving
- Using regulations to automate organization
- Scheduling
- Making public folders
- Using Quick Step
- Creating signatures
- Using Quick Parts
- Setting reminders
Microsoft Access
- Customizing, Creating, and sharing databases
- Making forms
- Building queries
- Importing and exporting data
- Filtering data
- Producing reports
- Converting reports to PDFs
21.Strategic thinking and problem-solving
Strategic planning and problem-solving are vital in today’s dynamic corporate climate. Managers use these skills to solve challenges, especially dynamic ones. Dynamic complexity differs from detail complexity since cause and effect are unclear, and intervention consequences are delayed. Strategic thinking is about recognizing and managing dynamic complexity. This form entails balancing market growth and capacity development, creating a lucrative blend of pricing, design, product quality, and accessibility, and sustainably enhancing quality and customer happiness. These strategic issues require profound understanding and deliberate solutions.
Strategic thinking and issue resolution include suspending critical thinking and analytical judgments to consider many options. Creative participation is essential for developing viable alternatives and solutions. Encouraging multiple perspectives helps firms create new, long-term strategic plans. Leaders should properly define their vision before tackling difficulties to ensure they answer the right questions. This technique helps create elegant, practical solutions that achieve goals. The video below can help u to improve strategic thinking.
22.Adaptability
Adaptability abilities allow you to adapt to new events and change your behavior while investing in a business newly. This requires strategic thought and openness to challenges. Any workplace has constructive criticism, unanticipated adjustments, and worst-case scenarios. Thus, adaptation is crucial. They help you decide and set goals. Adaptability lets you move forward instead of concentrating on problems.
Adaptability requires fresh circumstances, unlike flexibility, which is equally valuable. Work late or accommodate team members to show flexibility and adaptability. Regardless of your preparation, adapting is a unique scenario.
Personality-based, Cognitive, or emotional adaptability skills are expected. Cognitive adaptation requires digesting new information and changing one’s thinking. This adaptability type requires curiosity, openness, and learning. People with personality-based adaptability see situations as they are and adjust their actions accordingly. This helps in work by requiring communication, resourcefulness, and teamwork. Accepting and overcoming changes needs emotional adaptation and resilience.
Curiosity promotes growth and openness. Curious people are more willing to try new things and see challenges as learning opportunities. You’ll be curious about projects to improve your talents and foster workplace innovation. Learning rapidly and retaining knowledge, skills, and views helps you adjust to new conditions, whether alone or with others.
23.Asset allocation
Asset allocation is crucial to portfolio creation and balancing. It affects your overall results more than picking stocks. Choosing a portfolio mix of shares, bonds, funds, and real estate is dynamic. Your asset mix should represent your aims at any moment. Strategic Asset Allocation follows an essential policy mix of assets proportional to predicted returns for each asset class. Consider your risk level and investment timeframe. You can establish goals and rebalance your portfolio periodically.
Strategic asset allocation is like a buy-and-hold approach but emphasizes diversity to minimize risk and boost returns. A mix of 50% equities and 50% bonds would return 7.5% each year if stocks have returned 10% and bonds 5%. Strategic asset allocation usually involves buy-and-hold, even if asset values change and the policy mix changes. This can lead you to select constant-weighting asset allocation. This strategy rebalances your portfolio. You buy more of it, if an asset loses value. If the asset appreciates, you sell it.
A strategic asset allocation approach seem rigid for a long time. Therefore, you need to make short-term tactical changes to capitalize on unique or outstanding investing possibilities. A portfolio with market-timing relaxation allows you take part in economic situations that favor one asset class over another.
Tactical asset allocation is relatively active since the strategic asset mix is restored when short-term profits are realized. This technique requires discipline to identify when short-term opportunities have passed and adjust the portfolio to long-term assets.
24.Customer relationship management
A comprehensive skill set is needed to build strong, lasting client relationships as a Customer Relationship Manager (CRM). In 2024, CRMs must have interpersonal, logical, and strategic skills. This section covers the essential skills for CRMs, helping them fulfil changing client engagement and satisfaction needs.
Effective customer relationship management requires interpersonal and communication abilities. This skill set comprises empathy, active listening, and persuasive communication. A CRM must connect with customers, understand their needs, and present solutions that resonate. These talents depend on trust, devotion, dispute resolution, and consumer satisfaction. Strategic account management requires long-term thinking and client account management. This talent includes identifying development possibilities, setting account goals, and creating customized strategies that meet client and company goals. A strategic CRM can handle cross-selling, resources, and up-selling and keep sales pipelines healthy.
CRMs need problem-solving and analytical skills to give data-driven consumer solutions. This talent involves collecting and analyzing market trends, customer data, and feedback to understand client preferences. This skill helps CRMs recognize difficulties, anticipate problems, and provide strategic solutions that improve customer happiness and retention.
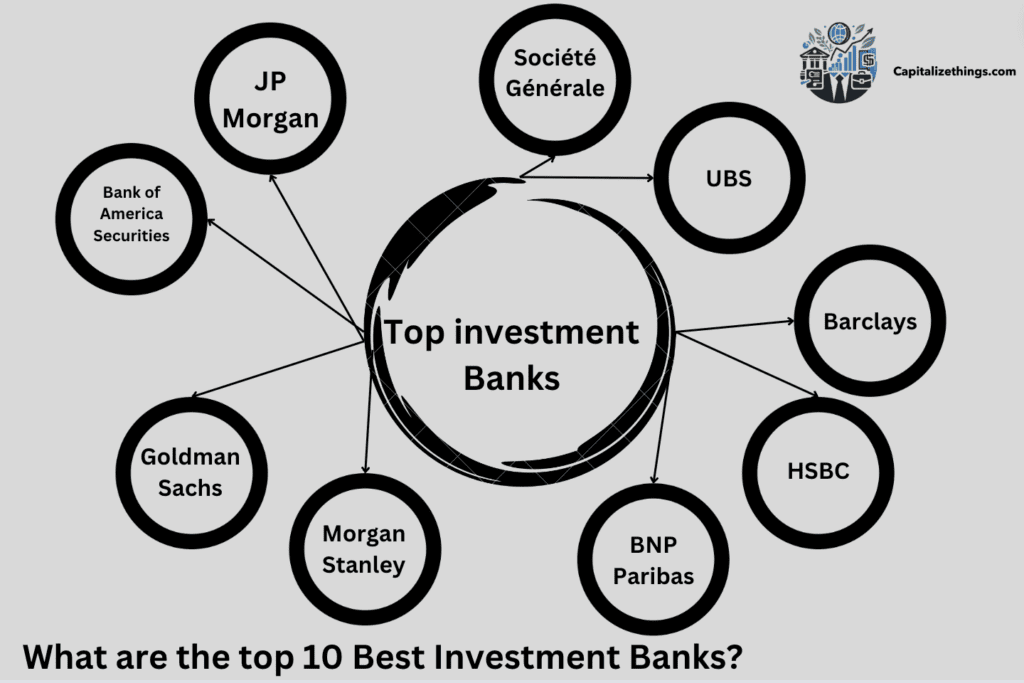
What are the top 10 Best Investment Banks?
Investment banks help companies with acquisitions and mergers (M&A) and provide market making, derivatives products and equity securities trading, FICC services, and research. Most investment banks have prime brokerage, asset management, and research on investments departments. The industry is divided into the Bulge Bracket (highest tier), Middle Market (mid-level), and boutique market. Institutional investors, governments, corporations, and others use investment banking for advice. A corporate finance bank underwrite or act as the client’s agent to issue debt or equity instruments to raise funds.
The List of top 10 Investment banks in the World:
- JP Morgan
- Bank of America Securities
- Goldman Sachs
- Morgan Stanley
- Citigroup
- BNP Paribas
- HSBC
- Barclays
- UBS
- Société Générale
The List of top 10 Investment banks in Europe
- Goldman Sachs
- Morgan Stanley
- J.P. Morgan
- Bank of America
- CITI
- Rothschild
- Lazard
- Barclays
- Deutsche
- BNP Paribas (mostly strong in Southern Europe)
The List of top 10 Investment banks in America
- JPMorgan Chase & Co
- Bank of America Corporation
- Wells Fargo
- Morgan Stanley
- Charles Schwab Corporation
- Goldman Sachs
- Citigroup
- US Bancorp
- PNC Financial Services
- Capital One Financial Corp
What are the different types of investment banks?
There are 3 types of Investment Banks. Investment banks are classed as middle-market, boutique, or bulge bracket. Boutique banks can be regional or exclusive.
- Boutique Banks
- Middle-Market Banks
- Bulge Bracket Banks
- Boutique Banks
There are elite boutique and regional investment banks. Elite boutique banks can resemble bulge bracket banks instead of regional boutiques. Regional boutique banks are the smallest investment banks compared to private equity in terms of size of company and deal size. Few to a few dozen people work at regional boutiques. Due to their size, most regional boutiques only provide some of the services of bulge bracket investment banks, including the most significant investment banks. Regional boutiques can concentrate on market sector acquisitions or mergers.
Elite boutique investment banks differ from regional boutiques. Elite boutiques, like bulge bracket banks, oversee agreements worth more than $1 billion, but they also handle lesser deals. Like bulge bracket banks, they have many nationwide offices. They need to gain the worldwide reach of investment banks like JPMorgan Chase. Elite boutiques, like regional boutiques, focus on M&A concerns rather than offering complete investment banking services. They offer restructuring and asset management more than regional.
- Middle-Market Banks
Middle-market investment banks fall between the bulge bracket and regional investment banks. Middle-market banks work on regional to bulge bracket investments from $50 million to a million dollars or more. Middle-market banks have a broader geographic reach than regional boutiques but less than bulge-bracket banks. Unlike boutique banks, middle-market banks offer the same equity and debt capital market services, banking and asset management, M&A, and restructuring activities as bulge bracket banks. Some middle-market banks specialize in one industry or sector, like regional boutiques. KBW, a middle-market investment bank that serves financial services companies, is well known.
- Bulge Bracket Banks
Central multinational investment banks are bulge bracket banks. The bulge bracket firms have the most offices, personnel, deals, and corporate clients. Most clients are Fortune 500 or 100 companies. Bulge bracket investment banks often control multibillion-dollar M&A deals, although based on the economy or client; they can handle deals in the millions. Each bulge bracket bank has globally and domestically significant operations. The central investment banks offer trading, asset management, various sorts of finance, issuance and equity research, and M&A services.
What does an investment banker do?
Investment bankers help corporate customers raise capital, advise them, and sometimes negotiate buying and selling. They range from entry-level to executive levels and are prized by corporations. With them, companies can raise funds to serve customers and build a strong market position.
What are the 4 main areas of investment banking?
The 4 main areas of investment banking are Capital Markets, Trading and Brokerage, Advisory, and Asset Management.
What is the difference between investment banking and hedge funds?
Hedge funds and Investment banking are different finance sectors. Investment banks help investees raise funds from investors. Hedge funds help wealthy institutions and individuals maximize their investments. Like asset managers, hedge funds use pooled vehicles (funds) to handle their clients’ money. Unlike mutual funds, hedge funds invest in complicated products and use sophisticated tactics. They test performance against no benchmark index and aim for absolute return regardless of market conditions. Alternative assets like hedge funds are riskier than mutual funds.
Investment banks finance public, private, institutional, and government clients. For a client’s stock offering, an investment bank underwrite (purchase the shares from the firm and resell them) or sell them through best efforts. Here, the client takes the risk. Banks can structure bond issues, advise on mergers and acquisitions, value firms, restructure enterprises, and raise cash through IPOs or secondary offers. Investment banks trade for institutions and private investors through their brokerage arm.
What is the difference between investment banking and asset management?
The difference between investment banking and asset management is that asset management maximizes returns based on the client’s risk tolerance and investment goals. Pension funds, foundations, endowments, governments, and high-net-worth individuals use a variety of asset classes and investment vehicles to increase their portfolios. Whereas Investment banking helps clients raise funds, manage significant financial transactions, and provide strategic advice. Investment banks serve governments, corporations, and other large entities that need help with complex transactions like M&A and public offerings.
Asset managers study market trends, handle portfolios, and make buy or sell choices based on research and the economy. Asset managers evaluate communicate and performance with clients regarding their investment portfolios. Investment bankers work in a faster-paced, project-driven atmosphere. Structure and negotiate large financial transactions, prepare pitch books, perform financial modeling, and communicate with stakeholders and clients to facilitate deals.
What is the difference between investment banking and commercial banking?
The difference between investment banking and commercial banking is that Unlike commercial banks, investment banks raise income by selling bonds and stocks. However, commercial banks use consumer deposits to fund credit and mortgages, and the interest earns them profit. These two financial entities overlap extensively.
Commercial banks offer corporations, governments, and institutions financial services and products. Large commercial banks have several subsidiaries with specialized products and services. JPMorgan Chase provides investment banking under JPMorgan, but commercial banking is under Chase Bank. Commercial banking frequently includes retail banking. Many larger banking institutes have investment banking divisions or companies, and most top investment banks are tied to commercial and retail banks. For instance, Citigroup Global Markets, Inc. handles investment banking and Citibank retail banking.
What is the difference between investment banking and consulting?
The difference between investment banking and consulting is that Investment banks assist corporations in conducting large financial transactions, whereas consulting firms help companies solve their biggest strategic problems. Thus, different industries have diverse skill sets, business structures, and lifestyles.
Young, talented, ambitious people want management consulting and investment banking careers. They offer intensive business training, significant entry-level compensation, and exit chances. Both industries advise big companies. They help organizations develop, change, and adapt to economic and political changes. Management consultants advise senior management on revenue growth, cost control, and organizational performance. Investment bankers finance corporations. Capital-raising services help organizations raise equity and debt. They also advise on mergers and acquisitions, assisting corporations to buy other companies or sell business units or the whole company.
What is the difference between investment banking and venture capital?
Venture capital firms fund start-ups and small businesses to help them prosper. Their investments earn them firm shares and a share of earnings. They also advise on company matters to define its direction. Investment bankers provide more clients with more services. They advise corporations on mergers, purchases, financial investments, and securities issuance. Due to their broad emphasis, they help many companies expand and reach financial goals.
Venture capitalists and investment banking professionals differ primarily in terms of investment patterns. Venture capitalists invest equity directly in a company, whereas investment bankers facilitate mergers, acquisitions, and other tasks. Both make money differently. Typically, venture capitalists want net profit from their start-up or small business investments. Venture capital firms usually sell their shares after the start-up has grown. Venture capital might get a significant return on their investment if the share offers more than they invested. However, investment banks prosper by charging fees for their services. The service they provide affect their price. Due to their broad range of services than the venture capitalists, they have various income sources. Investment bank fees can charge 3%-10% of the capital generated or mergers and acquisitions deal value.
What is the difference between investment banking and wealth management?
Investment bankers advise corporations, not individuals. They handle M&A, corporate restructuring, stock splits, spinoffs, share buybacks, IPOs, secondary stock issuance, and bond issues. They also manage corporate clients’ short-term investments.
The most excellent investment bankers manage organizations’ finances and negotiate multibillion-dollar acquisitions persuasively. They excel at leveraged buyouts and defending customers from hostile takeovers. Investment banking can be exciting, but it sometimes involves inaction. Investment bankers have to understand industry-specific elements that impact corporate success. Investment bankers must evaluate businesses fundamentally, whereas market analysts assess stocks.
Wealth management provides financial services primarily to high-net-worth and ultra-high-net-worth individuals, but less wealthy people sometimes use it. Some wealth managers work with $50,000–$500,000 clients, while others favor high-net-worth clients with millions. Wealth management means all sectors of finance management. Payment for services is how wealth management firms make money. Investment specialists at the firm often sell clients maintained account services and discretionary investment accounts that can be traded on their behalf.
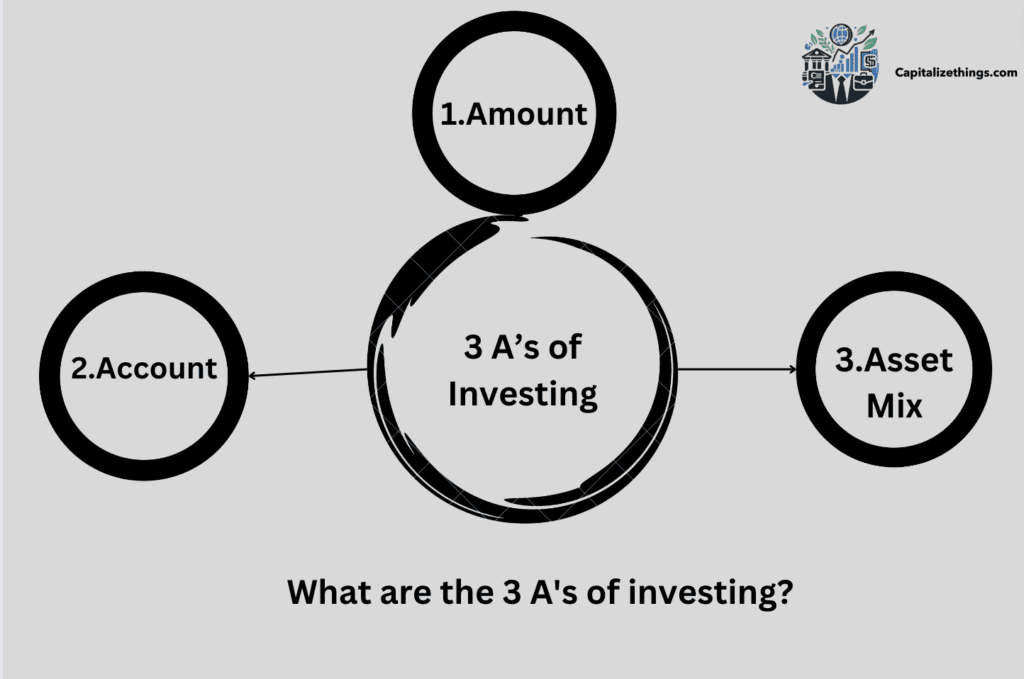
What are the 3 A’s of investing?
The 3 A’s or investing are amount, account and asset mix. Let’s dive into each together:
- Amount
- Account
- Asset mix
- Amount
Start saving early and aim to save 15% of pre-tax income each year to maintain your present lifestyle in retirement. Your employer’s matching or profit-sharing payments to your 401(k) or other workplace savings account, federal 457(b) or like a 403(b) plan, are included in that 15%. An employer match simplifies 15% savings. Elaine makes $50,000 a year, and her employer matches her contributions dollar for dollar up to 6% of compensation. She needs only 9%, or $4,500, to save 15% of her earnings, or $7,500. Her employer would give her $3,000 (6%). As you wait to start saving, maximizing your 401(k) contributions at every opportunity is crucial.
Your 401(k) can accept $23,000 pre-tax in 2024. If you’re 50 or older, you can make a $7,500 pre-tax catch-up contribution.
The 2024 Roth and regular IRA contribution limit is $7,000. If you’re older than 50, you can donate $1,000 annually. Health savings accounts (HSAs) are also tax-favored. A high-deductible health plan (HDHP) is required to open an HSA. The IRS limits HSA contributions to $4,149.99 for persons and $8,300 for families in 2024. Catch-up contributions are allowed up to $1,000 each year for those 55 and older. Your spouse, 55 or older, can make a catch-up payment but must open an HSA. If you cannot contribute 15% of your income right now, aim to receive the employer matching in a workplace account, which is “no-cost” money, and then increase your contributions as soon as possible.
- Account
Take advantage of 401(k), 403(b), and IRA retirement savings accounts. HSAs can be one of the best ways to save for eligible medical expenses now and in retirement if you have an HDHP. Payments can grow tax-free or tax-deferred, depending on the account. Pre-tax contributions to a typical 401(k) or IRA cut your taxable income and tax payment in the year you make them. You’ll pay income taxes on retirement withdrawals from your regular 401(k) or IRA.
Roth 401(k)s and IRAs work differently. You don’t pay taxes on Roth 401(k) or IRA withdrawals; contributions are made after tax. What form of 401(k) or IRA should someone contribute to—traditional or Roth? For many, the dilemma is: Am I better off making tax payments now or later? Those anticipating their retirement tax rate to be higher than their present rate benefit from tax-free Roth 401(k) or IRA withdrawals. A standard 401(k) or IRA is better for those who expect their retirement tax rate to drop. Some can benefit from contributing to both a regular and Roth account. That can help manage taxes by offering taxable and tax-free retirement withdrawal options. Those uncertain about their tax situation can make both sorts of contributions.
- Asset mix
Stocks have outpaced bonds and cash over time. Investing more in equities and stock mutual funds should make sense for a long-term goal like retirement. Stock investing involves increased volatility, so be prepared. We recommend a mix of investments according to your time horizon, finances, and risk tolerance. Long-term investors should have an extensive, diversified stock portfolio.
What are the fundamentals of investment?
Investing is buying assets you believe will raise. Investments involve purchasing a home, company, real estate, or bank and credit union savings accounts and CDs. A share of stock is a corporation share. If you acquire 100 GE shares, you own part of GE. Owning shares can reward you if the company pays dividends or their value rises. If the shares drop before you sell them, you can lose money. You lend money to the bond holders when you own one. If the bond appreciates and you earn interest, you profit. Buying mutual funds means buying shares in a company that owns equities in other companies or bonds from different companies or organizations. Mutual fund managers choose where and when to invest, so you get their expertise. You profit when the mutual fund provides dividends (and capital gains and interest) and its shares rise due to the stock and bond prices it owns.
There are several methods to invest. Most people start with brokerage, mutual fund, IRA, and employer retirement accounts. Investing through an individual account generates interest, taxable dividends, and capital gains. If the investments are in an IRA or qualifying plan, you can only pay taxes once you withdraw them.
What is investment banking for beginners?
Investment banking controls money flow. Investment banking puts money from new investors seeking returns into the hands of business builders and entrepreneurs with ideas but little cash. Many facets of investment banking obscure this goal. Investment bankers identify ways to unlock the value of firms or ideas, develop enterprises, or put idle money to work.
What is investment appraisal?
Investment appraisal analyzes an investment’s lifetime profits, accessibility, and strategic appropriateness. The project or program’s investment appraisal and business case depend on proper benefit attribution. The business case includes an investment analysis for the program, project, or portfolio and an evidence-based narrative of how the investment will deliver qualitative and quantitative benefits.
Comparing choices using an investment assessment that weighs whole-life expenses, advantages, and deployment risks to get the best value is expected. Project delivery can take weeks or years, and project benefit realization time can also vary greatly. The time value of money must be addressed for multi-year projects.
What is investment valuation?
Valuation is the process of determining an investment’s value. Financial statements, market circumstances, industry trends, and the economy are analyzed. Investment valuation helps investors identify fair prices and make informed judgments.
Should we diversify our investments?
Yes! We should diversify our investments. Most investing professionals think diversity is critical to achieving long-term financial goals while limiting risk.
Conclusion:
Investment banking advises and manages complex financial transactions involving firms, governments, and organizations. It also advises and facilitates mergers and acquisitions (M&As), including leveraged buyouts, underwrites debt financing, and issues equity securities in IPOs. The primary types are regional, elite boutique, middle-market, and bulge-bracket investment banks. Boutique businesses serve smaller clients, bulge bracket banks serve large corporations, and middle-market banks serve in between.
Many irrevocable investment decisions affect cash flows, growth, and profitability over the long term. Well-planned investments can yield high returns even with minimal funding. To enhance this talent, you must be able to write out the problem, develop a roadmap, ListList, weigh the possibilities, step back for a third-person perspective, set an end date, and use past decisions. Investment professionals examine financial data. Therefore, they must be meticulous. Their attention to detail might help those spot data issues and make intelligent investing selections. They should check all team information, too. Stay organized, make lists, stick to a schedule, and play focus-boosting games to improve this talent.
Investment professionals manage a company’s investment strategy’s finances. This covers risk assessment and mitigation. As investment experts, you need to recognize issues and find company-beneficial solutions. To perfect this talent, you must identify the problem, outline its essential aspects, study viable solutions, act on them, and search for lessons. Comparing company strategy to chess seems cliché, but it emphasizes strategic planning. However, in the business “game,” the board changes, and players start with different advantages. Strategically thinking companies constantly evaluate their benefits and weaknesses compared to their competitors to find the best opportunities to win.

Larry Frank is an accomplished financial analyst with over a decade of expertise in the finance sector. He holds a Master’s degree in Financial Economics from Johns Hopkins University and specializes in investment strategies, portfolio optimization, and market analytics. Renowned for his adept financial modeling and acute understanding of economic patterns, John provides invaluable insights to individual investors and corporations alike. His authoritative voice in financial publications underscores his status as a distinguished thought leader in the industry.